📘 Premium Read: Access my best content on Medium member-only articles — deep dives into Java, Spring Boot, Microservices, backend architecture, interview preparation, career advice, and industry-standard best practices.
🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (176K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
We'll create a simple version of the Library Management System with basic functionalities:
- Create a new User
- Fetch all the Users
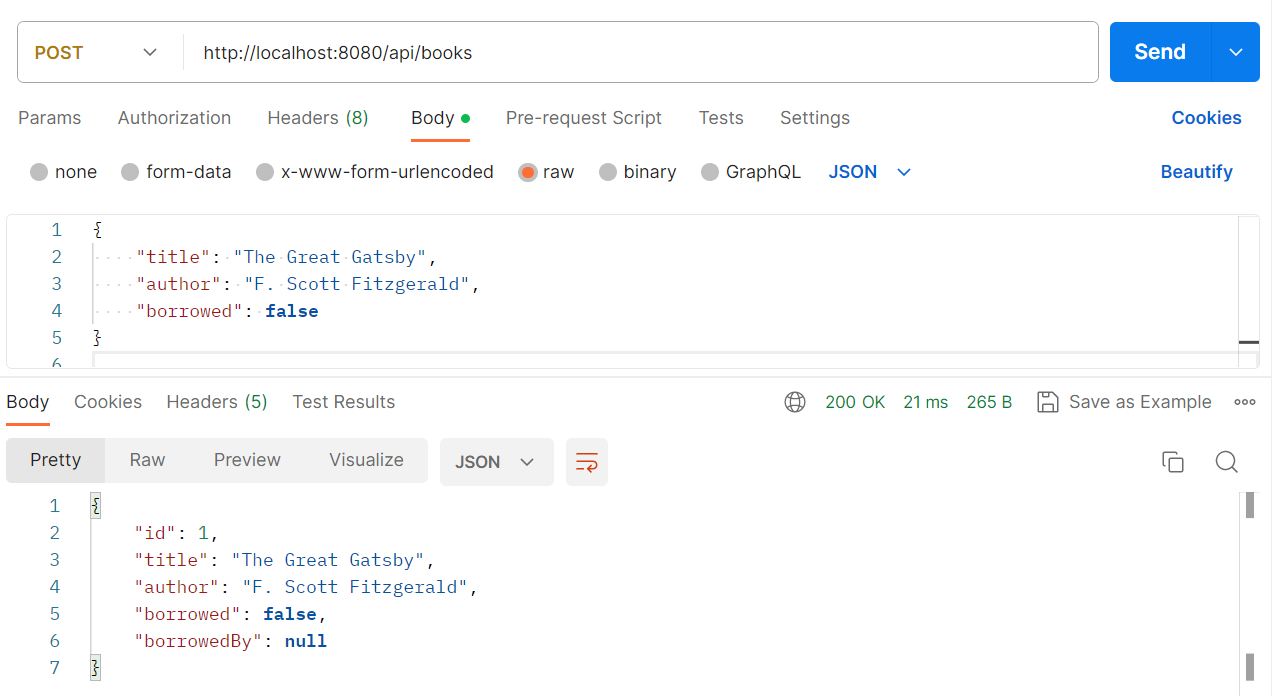
- Add new book
- Fetch all the books
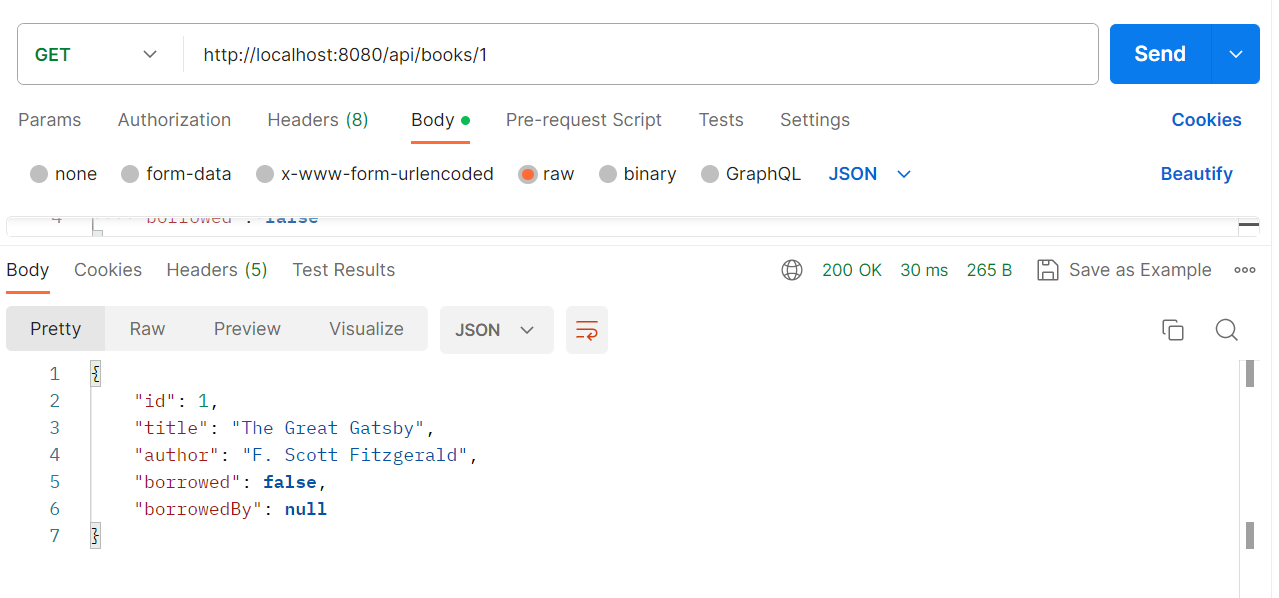
- Fetch specific book
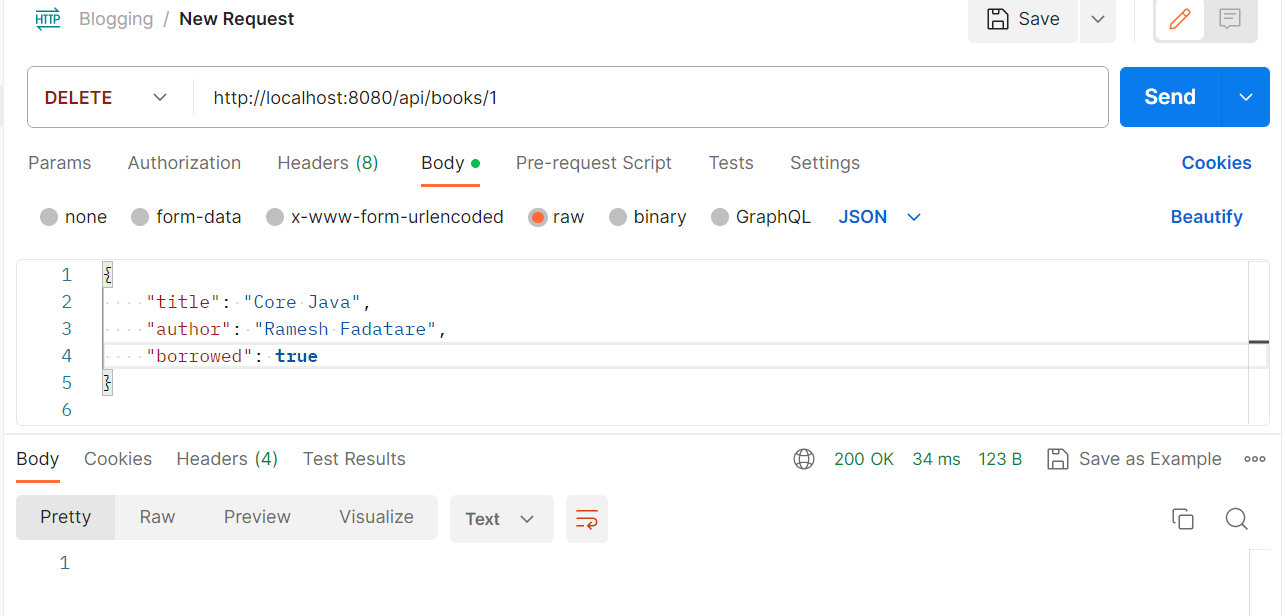
- Delete a book
- Borrow a book
- Return a book
1. Set up a Spring Boot project
Let's launch Spring Initializr and fill up the following project details:
Project: Maven Project (or Gradle)
Language: Java
Packaging: Jar
Java version: 17
Dependencies: Spring Web, Spring Data JPA, MySQL Driver, and Lombok
Download, extract the project, and import to your favorite IDE.
2. Configure the MySQL database
Let's open the src/main/resources/application.properties file and add the MySQL configuration properties:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/banking_app
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=Mysql@123
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=updateMake sure that you change the MySQL database username and password as per your MySQL installation on your machine.
The spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update line ensures that tables and columns get automatically created or updated based on your JPA entities.
3. Create JPA Entities
User
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
}Book
Let's create a Book JPA entity and add the following code to it:import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
@Entity
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String title;
private String author;
private boolean borrowed;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "user_id")
private User borrowedBy;
}
We added a relationship between the Book and User entities to track which user has borrowed a book.import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
@Entity
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String title;
private String author;
private boolean borrowed;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "user_id")
private User borrowedBy;
}4. Create Spring Data JPA Repositories
BookRepository
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.entity.Book;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface BookRepository extends JpaRepository<Book, Long> {
}UserRepository
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
}6. Create a Service Layer
BookService
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.entity.Book;
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.entity.User;
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.repository.BookRepository;
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.repository.UserRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public List<Book> findAll() {
return bookRepository.findAll();
}
public Book findById(Long id) {
return bookRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
public Book save(Book book) {
return bookRepository.save(book);
}
public void deleteById(Long id) {
bookRepository.deleteById(id);
}
public Book borrowBook(Long bookId, Long userId) {
Book book = findById(bookId);
User user = userRepository.findById(userId).orElse(null);
if (book != null && !book.isBorrowed() && user != null) {
book.setBorrowedBy(user);
book.setBorrowed(true);
return save(book);
}
// Handle errors (e.g., book not found, book already borrowed, user not found)
return null;
}
public Book returnBook(Long bookId) {
Book book = findById(bookId);
if (book != null && book.isBorrowed()) {
book.setBorrowedBy(null);
book.setBorrowed(false);
return save(book);
}
// Handle errors (e.g., book not found, book not borrowed)
return null;
}
}UserService
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.entity.User;
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.repository.UserRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public List<User> findAll() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
public User save(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
}7. Controller Layer
UserController
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.entity.User;
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
return userService.findAll();
}
@PostMapping
public User addUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.save(user);
}
}BookController
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.entity.Book;
import net.javaguides.bankingapp.service.BookService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@GetMapping
public List<Book> getAllBooks() {
return bookService.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Book getBook(@PathVariable Long id) {
return bookService.findById(id);
}
@PostMapping
public Book addBook(@RequestBody Book book) {
return bookService.save(book);
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public Book updateBook(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Book book) {
// Additional logic to ensure you're updating the correct book
return bookService.save(book);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void deleteBook(@PathVariable Long id) {
bookService.deleteById(id);
}
@PostMapping("/{bookId}/borrow/{userId}")
public ResponseEntity<Book> borrowBook(@PathVariable Long bookId, @PathVariable Long userId) {
Book borrowedBook = bookService.borrowBook(bookId, userId);
if (borrowedBook != null) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(borrowedBook);
} else {
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().build(); // or a more descriptive error response
}
}
@PostMapping("/{bookId}/return")
public ResponseEntity<Book> returnBook(@PathVariable Long bookId) {
Book returnedBook = bookService.returnBook(bookId);
if (returnedBook != null) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(returnedBook);
} else {
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().build(); // or a more descriptive error response
}
}
}Run and Test the Spring Boot Application
Navigate to the main application class (with @SpringBootApplication annotation) and run it as a Java application.
Add a new user:
Fetch all users:
Add a new book:
Fetch all books:
Fetch a specific book:
Delete a book:
Borrow a book:
Return a book:
GitHub
Conclusion
- Create a new User
- Fetch all the Users
- Add new book
- Fetch all the books
- Fetch specific book
- Delete a book
- Borrow a book
- Return a book




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)
















Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment