📘 Premium Read: Access my best content on Medium member-only articles — deep dives into Java, Spring Boot, Microservices, backend architecture, interview preparation, career advice, and industry-standard best practices.
🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (176K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
In this tutorial, we will learn how to build a simple Microservices project using Spring Boot 3, Spring Cloud, and PostgreSQL database.
In this microservices project, you'll explore essential concepts such as API Gateway, Config Server, Discovery Server, and hands-on implementation of two real-world microservices, Student and School.
Prerequisites
Ensure you have the following software installed on your system before proceeding:- Java Development Kit (JDK) 17 or later
- Maven
- Docker (optional, for containerization)
Microservices Architecture
Here is the Microservices Architecture for our Microservices project that we are going to build in this tutorial:
Let's understand the Microservices project components:
API Gateway
The API Gateway serves as the single entry point for all client requests, managing and routing them to the appropriate microservices.Config Server
The Config Server centralizes configuration management for all microservices, simplifying application maintenance and consistency across environments.Discovery Server
The Discovery Server provides service registration and discovery, enabling seamless service-to-service communication within the microservices ecosystem.Student Microservice
The Student Microservice is responsible for managing student-related data and operations, such as adding, updating, and retrieving student records.School Microservice
The School Microservice manages school-related data and operations, including adding, updating, and retrieving school records.Using OpenFeign - Inter-Service Communication
This project demonstrates inter-service communication using OpenFeign, a declarative REST client that simplifies service-to-service communication within the microservices ecosystem.Distributed Tracing - Using Zipkin
The project showcases the use of Zipkin for distributed tracing, enhancing application observability and enabling the visualization and troubleshooting of latency issues.1. Create Student Microservice
Let's build student microservice step by step.Create Spring Boot Project
Let's create a student microservice as a Spring boot project using the spring initializr.
Refer to the below screenshot to enter details while creating the spring boot application using the spring initializr:
Here is the complete pom.xml file for your reference:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>student</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>student</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Configure PostgreSQL Database
Create an application.yml file under /resources folder and add the following content:
Don’t forget to change the spring.datasource.username and spring.datasource.password as per your PostgreSQL installation. Also, create a database named students in PostgreSQL before proceeding to the next section.server: port: 8090 spring: application: name: students datasource: driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/students username: username password: password jpa: hibernate: ddl-auto: create database: postgresql database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
JPA Entity - Student
Let's create a Student JPA entity and add the following code to it:
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import lombok.*;
@Entity
@Getter
@Setter
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Integer id;
private String firstname;
private String lastname;
private String email;
private Integer schoolId;
}Repository Layer - StudentRepository
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentRepository extends JpaRepository<Student, Integer> {
List<Student> findAllBySchoolId(Integer schoolId);
}Service Layer - StudentService
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class StudentService {
private final StudentRepository repository;
public void saveStudent(Student student) {
repository.save(student);
}
public List<Student> findAllStudents() {
return repository.findAll();
}
public List<Student> findAllStudentsBySchool(Integer schoolId) {
return repository.findAllBySchoolId(schoolId);
}
}Controller Layer - StudentController
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/students")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class StudentController {
private final StudentService service;
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public void save(
@RequestBody Student student
) {
service.saveStudent(student);
}
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<List<Student>> findAllStudents() {
return ResponseEntity.ok(service.findAllStudents());
}
@GetMapping("/school/{school-id}")
public ResponseEntity<List<Student>> findAllStudents(
@PathVariable("school-id") Integer schoolId
) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(service.findAllStudentsBySchool(schoolId));
}
}That's completed our student microservice development.
2. Create School Microservice
Create Spring Boot Project
Let's create a school microservice as a Spring boot project using the spring initializr.
Refer to the below screenshot to enter details while creating the spring boot application using the spring initializr:
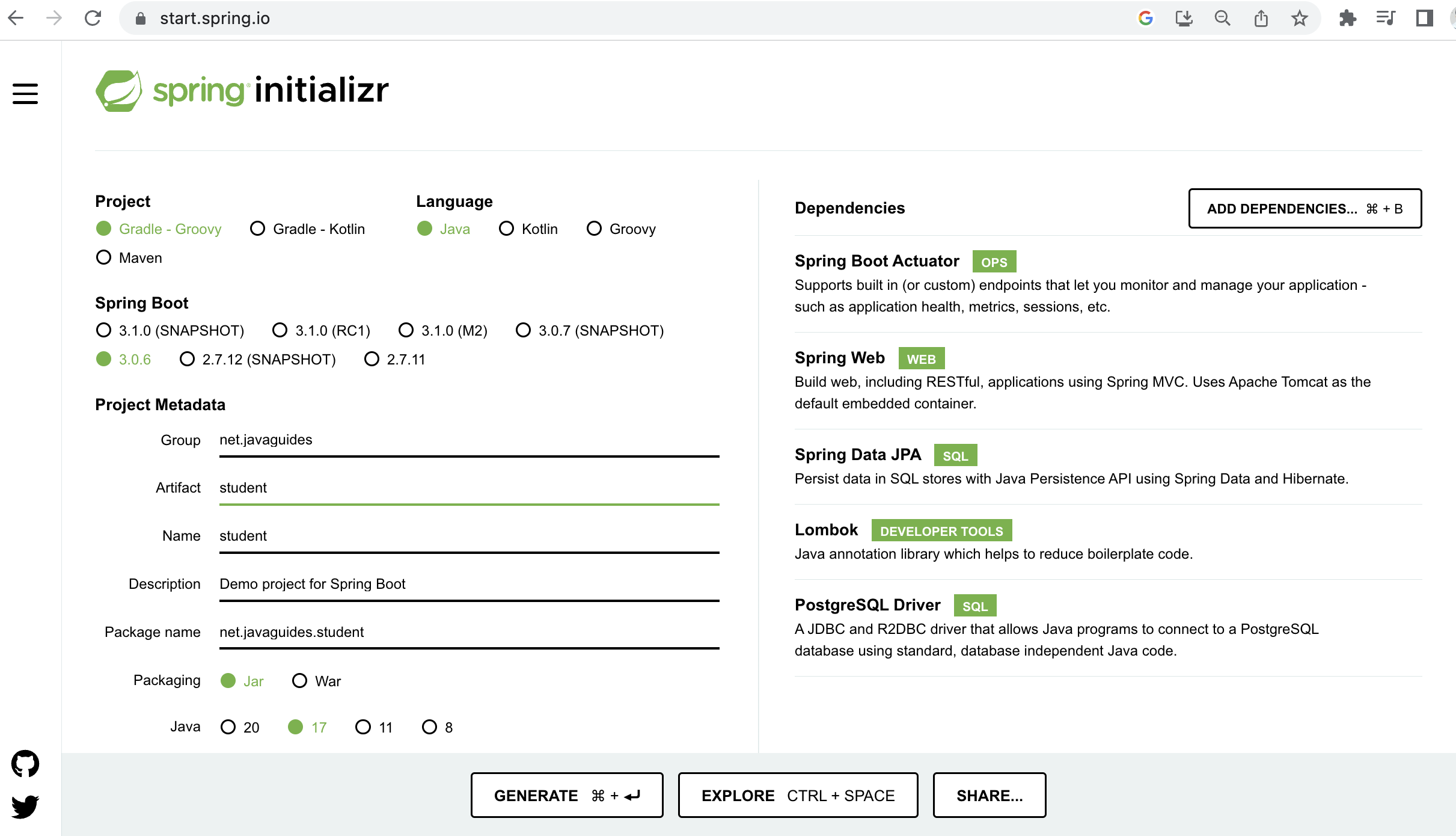
Here is the complete pom.xml file for your reference:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>school</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>school</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Configure PostgreSQL Database
Create an application.yml file under /resources folder and add the following content:
server:
port: 8090
spring:
application:
name: schools
datasource:
driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/students
username: username
password: password
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create
database: postgresql
database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialectDomain Layer - School JPA Entity
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import lombok.*;
@Entity
@Getter
@Setter
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class School {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String email;
}Repository Layer - SchoolRepository
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface SchoolRepository extends JpaRepository<School, Integer> {
}Create a DTO Class
import lombok.*;
import java.util.List;
@Getter
@Setter
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class FullSchoolResponse {
private String name;
private String email;
List<Student> students;
}Service Layer - SchoolService
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SchoolService {
private final SchoolRepository repository;
private final StudentClient client;
public void saveSchool(School school) {
repository.save(school);
}
public List<School> findAllSchools() {
return repository.findAll();
}
}Controller Layer - SchoolController
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/schools")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SchoolController {
private final SchoolService service;
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public void save(
@RequestBody School school
) {
service.saveSchool(school);
}
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<List<School>> findAllSchools() {
return ResponseEntity.ok(service.findAllSchools());
}
}3. Using OpenFeign - Inter-Service Communication
Add OpenFeign Dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>Make sure to add spring cloud dependencies and their version.
Here is the complete pom.xml file after adding Spring cloud open feign dependency:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>school</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>school</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2022.0.2</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Enable OpenFeign Client in School Service
Next, let's enable OpenFeign Client using @EnableFeignClients annotation:import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@EnableFeignClients
@SpringBootApplication
public class SchoolApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SchoolApplication.class, args);
}
}Create feign API client
After that, we need to have a feign API client with the necessary methods, requests, and responses.Let's create an interface named StudentClient and add the following code:
import net,javaguides.school.Student;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import java.util.List;
@FeignClient(name = "student-service", url = "${application.config.students-url}")
public interface StudentClient {
@GetMapping("/school/{school-id}")
List<Student> findAllStudentsBySchool(@PathVariable("school-id") Integer schoolId);
}Change SchoolService Class
public FullSchoolResponse findSchoolsWithStudents(Integer schoolId) {
var school = repository.findById(schoolId)
.orElse(
School.builder()
.name("NOT_FOUND")
.email("NOT_FOUND")
.build()
);
var students = client.findAllStudentsBySchool(schoolId);
return FullSchoolResponse.builder()
.name(school.getName())
.email(school.getEmail())
.students(students)
.build();
}Note that we are using the OpenFeign client to make a REST API call:
var students = client.findAllStudentsBySchool(schoolId);Here is the complete StudentService class code:
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SchoolService {
private final SchoolRepository repository;
private final StudentClient client;
public void saveSchool(School school) {
repository.save(school);
}
public List<School> findAllSchools() {
return repository.findAll();
}
public FullSchoolResponse findSchoolsWithStudents(Integer schoolId) {
var school = repository.findById(schoolId)
.orElse(
School.builder()
.name("NOT_FOUND")
.email("NOT_FOUND")
.build()
);
var students = client.findAllStudentsBySchool(schoolId);
return FullSchoolResponse.builder()
.name(school.getName())
.email(school.getEmail())
.students(students)
.build();
}
}Create REST API - Retrieve Students by School Id
@GetMapping("/with-students/{school-id}")
public ResponseEntity<FullSchoolResponse> findAllStudentsBySchoolId(
@PathVariable("school-id") Integer schoolId
) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(service.findSchoolsWithStudents(schoolId));
}Here is the complete SchoolController class code:
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/schools")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SchoolController {
private final SchoolService service;
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public void save(
@RequestBody School school
) {
service.saveSchool(school);
}
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<List<School>> findAllSchools() {
return ResponseEntity.ok(service.findAllSchools());
}
@GetMapping("/with-students/{school-id}")
public ResponseEntity<FullSchoolResponse> findAllStudentsBySchoolId(
@PathVariable("school-id") Integer schoolId
) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(service.findSchoolsWithStudents(schoolId));
}
}4. Discovery
In this section, we will learn how to use SpringCloud Netflix Eureka for Service Registry and Discovery.
Create Spring Boot Project
Let's create a Spring boot project using the spring initializr.
Refer to the below screenshot to enter details while creating the spring boot application using the spring initializr:
Here is the complete pom.xml file for your reference:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>discovery</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>discovery</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2022.0.2</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>netflix-candidates</id>
<name>Netflix Candidates</name>
<url>https://artifactory-oss.prod.netflix.net/artifactory/maven-oss-candidates</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
</project>Add @EnableEurekaServer annotation
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class DiscoveryApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DiscoveryApplication.class, args);
}
}Configure the Eureka Server in an application.yml File
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
register-with-eureka: false
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
server:
port: 8761Registering Student Microservice as Eureka Client
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eurekaRegistering School Microservice as Eureka Client
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eurekaRun Discovery Service
With this configuration in place, start the discovery service and visit http://localhost:8761:
5. API Gateway
In this section, we will learn how to set up an API gateway into our microservices project using the Spring Cloud Gateway library.
Spring Cloud Gateway provides a library for building an API Gateway on top of Spring WebFlux. Spring Cloud Gateway aims to provide a simple, yet effective way to route to APIs and provide cross-cutting concerns to them such as security, monitoring/metrics, and resiliency.
Create Spring Boot Project
Let's create a Spring boot project using the spring initializr.
Refer to the below screenshot to enter details while creating the spring boot application using the spring initializr:
Here is the complete pom.xml file for your reference:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>gateway</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>gateway</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2022.0.2</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>netflix-candidates</id>
<name>Netflix Candidates</name>
<url>https://artifactory-oss.prod.netflix.net/artifactory/maven-oss-candidates</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
</project>Configuring API Gateway Routes With Spring Cloud Gateway
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false
server:
port: 8222
spring:
application:
name: gateway
cloud:
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true
routes:
- id: students
uri: http://localhost:8090
predicates:
- Path=/api/v1/students/**
- id: schools
uri: http://localhost:8070
predicates:
- Path=/api/v1/schools/**
management:
tracing:
sampling:
probability: 1.06. Config Server
In this section, we will learn how to create a Spring cloud config server to centralize configurations of the Spring boot microservices.
Well, we will keep the configuration files of all the microservices in a local central place.
Create Spring Boot Project
Let's create a Spring boot project using the spring initializr.
Refer to the below screenshot to enter details while creating the spring boot application using the spring initializr:
Here is the pom.xml file for your reference:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>config-server</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>config-server</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2022.0.2</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Enable Config Server using @EnableConfigServer Annotation
To make our Spring Boot application a Spring Cloud Config Server, we just need to add the @EnableConfigServer annotation to the main entry point class:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
@EnableConfigServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args);
}
}Configure the Location for Centralized Configuration
Now, let's configure the location of the local repository where we are going to store all our configuration files in the application.properties file:
server:
port: 8888
spring:
profiles:
active: native
application:
name: config-server
cloud:
config:
server:
native:
search-locations: classpath:/configurationsUnder /resources/configurations folder and keep all the configuration files:
students.yml
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka
server:
port: 8090
spring:
application:
name: students
datasource:
driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/students
username: username
password: password
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create
database: postgresql
database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
management:
tracing:
sampling:
probability: 1.0School.yml
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka
server:
port: 8070
spring:
application:
name: schools
datasource:
driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/schools
username: username
password: password
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create
database: postgresql
database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
application:
config:
students-url: http://localhost:8222/api/v1/students
management:
tracing:
sampling:
probability: 1.0
discovery.yml
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost
client:
register-with-eureka: false
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
server:
port: 8761gateway.yml
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false
server:
port: 8222
spring:
application:
name: gateway
cloud:
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true
routes:
- id: students
uri: http://localhost:8090
predicates:
- Path=/api/v1/students/**
- id: schools
uri: http://localhost:8070
predicates:
- Path=/api/v1/schools/**
management:
tracing:
sampling:
probability: 1.0Refactor the Student Service to use Config Server
Add the below dependency to the student service pom.xml file to use the config server:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>Configure config server URL in student service
spring:
application:
name: students
config:
import: optional:configserver:http://localhost:8888Refactor the School Service to use Config Server
Add the below dependency to the school service pom.xml file to use the config server:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>Configure config server URL in School service
spring:
application:
name: students
config:
import: optional:configserver:http://localhost:8888Refactor the Discovery Service to use Config Server
Add the below dependency to the discovery service pom.xml file to use the config server:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>Configure config server URL in Discovery service
spring:
application:
name: students
config:
import: optional:configserver:http://localhost:8888Refactor the Gateway Service to use Config Server
Add the below dependency to the gateway service pom.xml file to use the config server:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>Configure config server URL in Gateway service
spring:
application:
name: students
config:
import: optional:configserver:http://localhost:8888Demo
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how to build a step-by-step microservice project using Spring Boot 3, Spring Cloud, and the PostgreSQL database.
Credits
You can check out the complete source on the GitHub repository: https://github.com/ali-bouali/springboot-3-micro-service-demo.
Video tutorial available here: Microservices tutorial with Spring boot 3 | Full course




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)


















Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment