In a previous couple of tutorials, we have seen:
Spring Boot Microservices Communication Example using RestTemplate
Spring Boot Microservices Communication Example using WebClient
Spring Boot Microservices Communication Example using Spring Cloud Open Feign
Spring Boot Microservices - Spring Cloud Config Server
Spring Boot Microservices - Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka-based Service Registry
YouTube Video
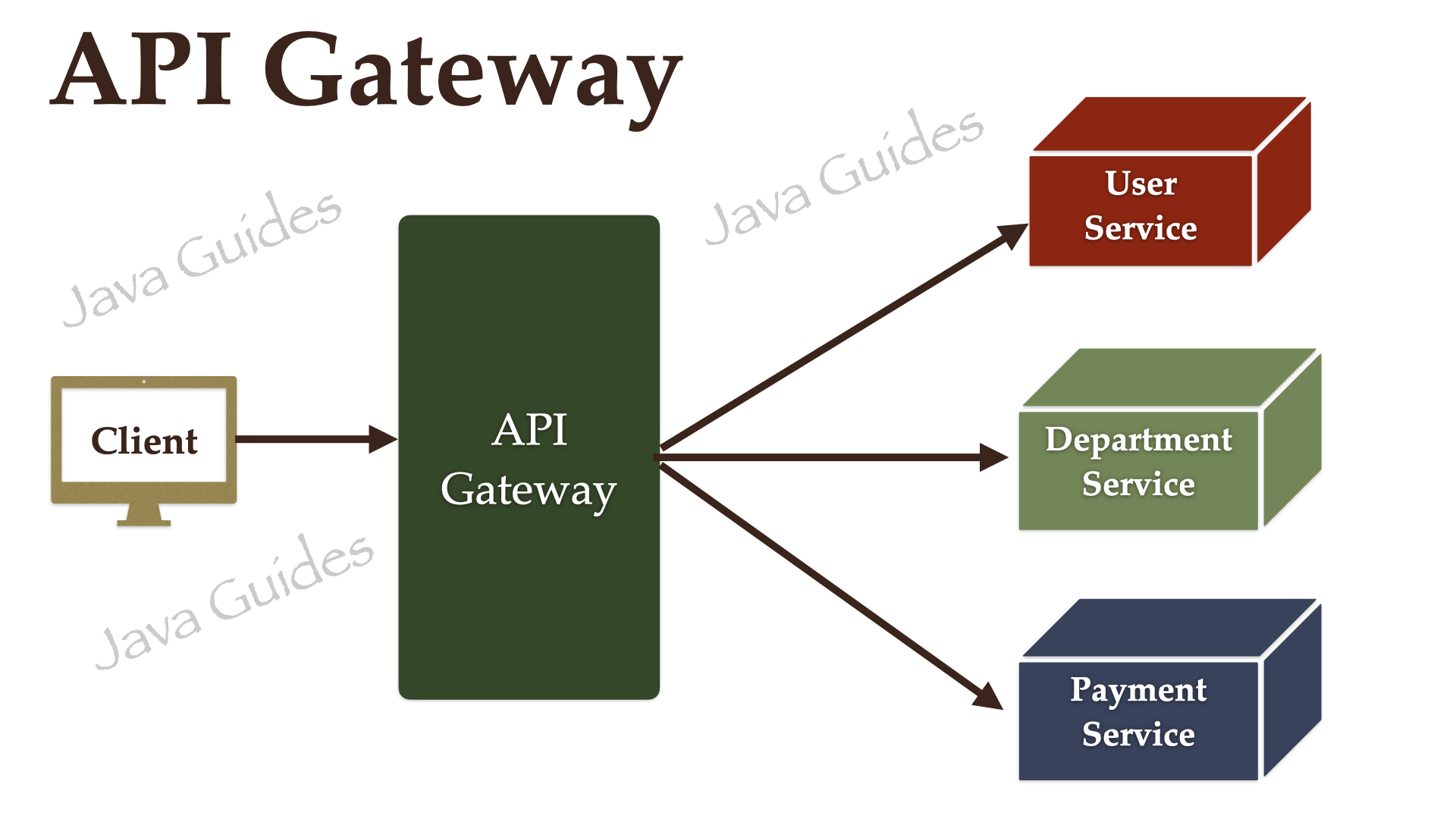
Spring Cloud Gateway Overview
Spring Cloud Gateway provides a library for building an API Gateway on top of Spring WebFlux. Spring Cloud Gateway aims to provide a simple, yet effective way to route to APIs and provide cross-cutting concerns to them such as security, monitoring/metrics, and resiliency.Prerequisites
1. Create and Setup Spring Boot Project in IntelliJ IDEA
Let's create a Spring boot project using the spring initializr.
Refer to the below screenshot to enter details while creating the spring boot application using the spring initializr:
Here is the pom.xml file for your reference:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>nt.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>api-gateway</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>api-gateway</name>
<description>api-gateway</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2021.0.4</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Now we have all the dependencies that we need to have in our API gateway application. So now let’s configure the Routes and other API gateway-specific configurations to use in our project.
2. Enable Eureka Client using @EnableEurekaClient
package nt.javaguides.apigateway;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class ApiGatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ApiGatewayApplication.class, args);
}
}3. Configure Eureka Server URL
To register the Spring Boot application into Eureka Server we need to add the following configuration in our application.properties file and specify the Eureka Server URL in our configuration.spring.application.name=API-GATEWAY
server.port=9191
eureka.instance.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*4. Configuring API Gateway Routes With Spring Cloud Gateway
Now, you might be wondering how API Gateway knows the hostname or IP and port of microservices right.
When a client sends a request to the API gateway, It will discover the correct service IP and PORT using the service registry to communicate and route the request.
Let's configure Routes using properties:spring.application.name=API-GATEWAY
server.port=9191
eureka.instance.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
spring.cloud.gateway.routes[0].id=USER-SERVICE
spring.cloud.gateway.routes[0].uri=lb://USER-SERVICE
spring.cloud.gateway.routes[0].predicates[0]=Path=/api/users/**
spring.cloud.gateway.routes[1].id=DEPARTMENT-SERVICE
spring.cloud.gateway.routes[1].uri=lb://DEPARTMENT-SERVICE
spring.cloud.gateway.routes[1].predicates[0]=Path=/api/departments/**
spring.cloud.gateway.routes[2].id=DEPARTMENT-SERVICE
spring.cloud.gateway.routes[2].uri=lb://DEPARTMENT-SERVICE
spring.cloud.gateway.routes[2].predicates[0]=Path=/message/**What are the properties that we set for API gateway routes?
- id – This is just an identification of the routes.
- URI – Here we can use either URL http://localhost:8080 or lb://DEPARTMENT-SERVICE. But if we need to use the inbuilt load balancer on the Netflix Eureka server, we should use lb://DEPARTMENT-SERVICE, then the API registry will take over the request and show a load-balanced request destination to the API gateway.
- predicates – In here we can set multiple paths to identify a correct routing destination. Eg:- If the API gateway gets and request like http://localhost:9191/api/users/1 then it will be routed into http://localhost:8081/api/users/1.
5. Run All the Microservices
Department Service running on port: http://localhost:8080
User Service running on port: http://localhost:8081
API Gateway service running on port: http://localhost:9191
Service Registry service running on port: http://localhost:8761
6. Verify Registered Instances in Service Registry
7. Testing API Gateway using Postman Client
Get Department REST API:
Department Service running on port: http://localhost:8080
API Gateway service running on port: http://localhost:9191
API Gateway route the request from http://localhost:9191/api/departments/1 to http://localhost:8080/api/departments/1
Get User REST API:
Note that we are using API-Gateway service port (9191) to call the user-service API port (8081).
User Service running on port: http://localhost:8081
API Gateway service running on port: http://localhost:9191
API Gateway route the request from http://localhost:9191/api/users/1 to http://localhost:8081/api/users/1
8. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how to set up an API gateway into our microservices project using the Spring Cloud Gateway library.Related Tutorials
✅ Spring Boot Microservices Communication Example using RestTemplate
✅ Spring Boot Microservices Communication Example using WebClient
✅ Spring Boot Microservices Communication Example using Spring Cloud Open Feign
✅ Spring Boot Microservices - Spring Cloud Config Server
✅ Spring Boot Microservices - Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka-based Service Registry





Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment