📘 Premium Read: Access my best content on Medium member-only articles — deep dives into Java, Spring Boot, Microservices, backend architecture, interview preparation, career advice, and industry-standard best practices.
🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (176K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
In this tutorial, we will learn how to build a CRUD full-stack application using Angular as frontend and Spring boot as backend. We will use MongoDB as a NoSQL database.
Spring Boot is an opinionated framework that helps developers build Spring-based applications quickly and easily. The main goal of Spring Boot is to quickly create Spring-based applications without requiring developers to write the same boilerplate configuration again and again.
Angular is a platform and framework for building single-page client applications using HTML and TypeScript. Angular is written in TypeScript. It implements core and optional functionality as a set of TypeScript libraries that you import into your applications.MongoDB is a document database with the scalability and flexibility that you want with the querying and indexing that you need.
Pre-requisites
In this tutorial, we will build CRUD Angular application that consumes REST APIs exposed in Spring Boot + MongoDB CRUD Example Tutorial tutorial.
Architecture
What we will build?
- springboot-backend: Develop and expose REST APIs. For building REST APIs, refer to Spring Boot MongoDB CRUD Example tutorial.
- angular-frontend: Consume REST APIs that are exposed by Spring boot REST APIs.
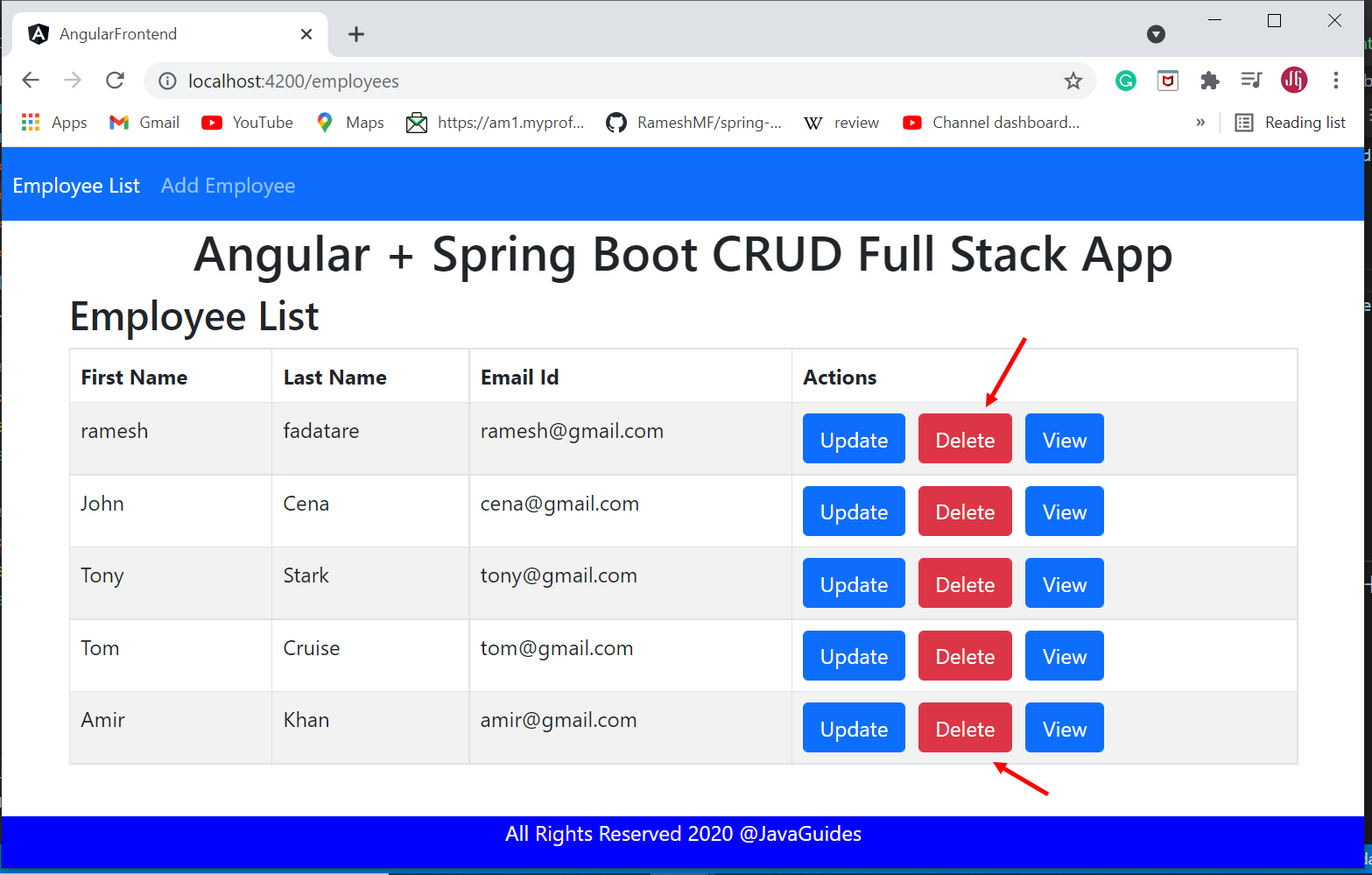
Employee List Page
Add Employee Page
Update Employee Page
Building Angular Frontend Application
G:\angular\Angular 12>node -v
v12.18.2
G:\angular\Angular 12>npm -v
6.14.51. Install the latest version of Angular CLI
npm install -g @angular/cli
G:\angular\Angular 12>ng --version
_ _ ____ _ ___
/ \ _ __ __ _ _ _| | __ _ _ __ / ___| | |_ _|
/ △ \ | '_ \ / _` | | | | |/ _` | '__| | | | | | |
/ ___ \| | | | (_| | |_| | | (_| | | | |___| |___ | |
/_/ \_\_| |_|\__, |\__,_|_|\__,_|_| \____|_____|___|
|___/
Angular CLI: 12.1.3
Node: 12.18.2
Package Manager: npm 6.14.5
OS: win32 x64
Angular:
...
Package Version
------------------------------------------------------
@angular-devkit/architect 0.1201.3 (cli-only)
@angular-devkit/core 12.1.3 (cli-only)
@angular-devkit/schematics 12.1.3 (cli-only)
@schematics/angular 12.1.3 (cli-only)2. Create Angular App using Angular CLI
ng new angular-frontend3. Identify Components, Services, and Modules
Components
- create-employee
- update-employee
- employee-list
- employee-details
Services
- employee.service.ts - Service for HTTP Client methods
Modules
- FormsModule
- HttpClientModule
- AppRoutingModule
Employee Class (Typescript class)
- employee.ts: class Employee (id, firstName, lastName, emailId)
4. Create Angular Components and Service Classes using Angular CLI
– ng g c create-employee
– ng g c update-employee
– ng g c employee-details
– ng g c employee-list
- ng g s employee5. Integrate JQuery and Bootstrap with Angular
npm install bootstrap jquery --save
...
"styles": [
"src/styles.css",
"node_modules/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"
],
"scripts": [
"node_modules/jquery/dist/jquery.min.js",
"node_modules/bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap.min.js"
]
...
/* You can add global styles to this file, and also import other style files */
@import '~bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css';
.footer {
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
width:100%;
height: 70px;
background-color: blue;
text-align: center;
color: white;
}6. Create an Employee Model (TypeScript)
export class Employee {
id: number;
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
emailId: string;
}7. Create Employee Service - REST Client
Path - src/app/employee.service.tsThe EmployeeService will be used to get the data from the backend by calling spring boot APIs. Update the employee.service.ts file inside src/app directory with the following code to it -import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http'
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
import { Employee } from './employee';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class EmployeeService {
private baseURL = "http://localhost:8080/api/v1/employees";
constructor(private httpClient: HttpClient) { }
getEmployeesList(): Observable<Employee[]>{
return this.httpClient.get<Employee[]>(`${this.baseURL}`);
}
createEmployee(employee: Employee): Observable<Object>{
return this.httpClient.post(`${this.baseURL}`, employee);
}
getEmployeeById(id: number): Observable<Employee>{
return this.httpClient.get<Employee>(`${this.baseURL}/${id}`);
}
updateEmployee(id: number, employee: Employee): Observable<Object>{
return this.httpClient.put(`${this.baseURL}/${id}`, employee);
}
deleteEmployee(id: number): Observable<Object>{
return this.httpClient.delete(`${this.baseURL}/${id}`);
}
}
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http'
import { Observable } from 'rxjs';
import { Employee } from './employee';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class EmployeeService {
private baseURL = "http://localhost:8080/api/v1/employees";
constructor(private httpClient: HttpClient) { }
getEmployeesList(): Observable<Employee[]>{
return this.httpClient.get<Employee[]>(`${this.baseURL}`);
}
createEmployee(employee: Employee): Observable<Object>{
return this.httpClient.post(`${this.baseURL}`, employee);
}
getEmployeeById(id: number): Observable<Employee>{
return this.httpClient.get<Employee>(`${this.baseURL}/${id}`);
}
updateEmployee(id: number, employee: Employee): Observable<Object>{
return this.httpClient.put(`${this.baseURL}/${id}`, employee);
}
deleteEmployee(id: number): Observable<Object>{
return this.httpClient.delete(`${this.baseURL}/${id}`);
}
}8. Creating Employee List Component and Template
Path - src/app/employee-list/employee-list.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Employee } from '../employee'
import { EmployeeService } from '../employee.service'
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-employee-list',
templateUrl: './employee-list.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./employee-list.component.css']
})
export class EmployeeListComponent implements OnInit {
employees: Employee[];
constructor(private employeeService: EmployeeService,
private router: Router) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
this.getEmployees();
}
private getEmployees(){
this.employeeService.getEmployeesList().subscribe(data => {
this.employees = data;
});
}
employeeDetails(id: number){
this.router.navigate(['employee-details', id]);
}
updateEmployee(id: number){
this.router.navigate(['update-employee', id]);
}
deleteEmployee(id: number){
this.employeeService.deleteEmployee(id).subscribe( data => {
console.log(data);
this.getEmployees();
})
}
}Path - src/app/employee-list/employee-list.component.html
<div class = "row">
<h2> Employee List</h2>
</div>
<table class = "table table-striped table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th> First Name</th>
<th> Last Name </th>
<th> Email Id</th>
<th> Actions </th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr *ngFor = "let employee of employees" >
<td> {{ employee.firstName }} </td>
<td> {{ employee.lastName }} </td>
<td> {{ employee.emailId }} </td>
<td>
<button (click) = "updateEmployee(employee.id)" class = "btn btn-primary"> Update</button>
<button (click) = "deleteEmployee(employee.id)" class = "btn btn-danger" style="margin-left: 10px"> Delete</button>
<button (click) = "employeeDetails(employee.id)" class = "btn btn-primary" style="margin-left: 10px"> View</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>9. Create Add Employee Component and Template
Path - src/app/create-employee/create-employee.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Employee } from '../employee';
import { EmployeeService } from '../employee.service';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-create-employee',
templateUrl: './create-employee.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./create-employee.component.css']
})
export class CreateEmployeeComponent implements OnInit {
employee: Employee = new Employee();
constructor(private employeeService: EmployeeService,
private router: Router) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
saveEmployee(){
this.employeeService.createEmployee(this.employee).subscribe( data =>{
console.log(data);
this.goToEmployeeList();
},
error => console.log(error));
}
goToEmployeeList(){
this.router.navigate(['/employees']);
}
onSubmit(){
console.log(this.employee);
this.saveEmployee();
}
}Path - src/app/create-employee/create-employee.component.html
<div class="row">
<div class="card col-md-6 offset-md-3 offset-md-3">
<div class="row">
<h3 class="text-center"> Create Employee </h3>
<hr />
<div class="card-body">
<form (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()">
<div class="form-group">
<label> First Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="firstName" [(ngModel)]="employee.firstName"
name="firstName">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label> Last Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="lastName" [(ngModel)]="employee.lastName"
name="lastName">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label> Email Id</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="emailId" [(ngModel)]="employee.emailId"
name="emailId">
</div>
<br />
<button class="btn btn-success" type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>10. Create Update Employee Component and Template
Path - src/app/update-employee/update-employee.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { EmployeeService } from '../employee.service';
import { Employee } from '../employee';
import { ActivatedRoute, Router } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-update-employee',
templateUrl: './update-employee.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./update-employee.component.css']
})
export class UpdateEmployeeComponent implements OnInit {
id: number;
employee: Employee = new Employee();
constructor(private employeeService: EmployeeService,
private route: ActivatedRoute,
private router: Router) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
this.id = this.route.snapshot.params['id'];
this.employeeService.getEmployeeById(this.id).subscribe(data => {
this.employee = data;
}, error => console.log(error));
}
onSubmit(){
this.employeeService.updateEmployee(this.id, this.employee).subscribe( data =>{
this.goToEmployeeList();
}
, error => console.log(error));
}
goToEmployeeList(){
this.router.navigate(['/employees']);
}
}Path - src/app/update-employee/update-employee.component.html
<div class="row">
<div class="card col-md-6 offset-md-3 offset-md-3">
<div class="row">
<h3 class="text-center"> Update Employee </h3>
<hr />
<div class="card-body">
<form (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()">
<div class="form-group">
<label> First Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="firstName" [(ngModel)]="employee.firstName"
name="firstName">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label> Last Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="lastName" [(ngModel)]="employee.lastName"
name="lastName">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label> Email Id</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="emailId" [(ngModel)]="employee.emailId"
name="emailId">
</div>
<br />
<button class="btn btn-success" type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>11. Create View Employee Details Component and Template
Path - src/app/employee-details/employee-details.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Employee } from '../employee';
import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router';
import { EmployeeService } from '../employee.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-employee-details',
templateUrl: './employee-details.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./employee-details.component.css']
})
export class EmployeeDetailsComponent implements OnInit {
id: number
employee: Employee
constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute, private employeService: EmployeeService) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
this.id = this.route.snapshot.params['id'];
this.employee = new Employee();
this.employeService.getEmployeeById(this.id).subscribe( data => {
this.employee = data;
});
}
}Path - src/app/employee-details/employee-details.component.html
<h3> View Employee Details</h3>
<div>
<div>
<label> <b> First Name: </b></label> {{employee.firstName}}
</div>
<div>
<label> <b> Last Name: </b></label> {{employee.lastName}}
</div>
<div>
<label> <b> Email Id: </b></label> {{employee.emailId}}
</div>
</div>12. package.json - Configure Dependencies
Path: /package.json
{
"name": "angular-frontend",
"version": "0.0.0",
"scripts": {
"ng": "ng",
"start": "ng serve",
"build": "ng build",
"watch": "ng build --watch --configuration development",
"test": "ng test"
},
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
"@angular/animations": "~12.1.0-",
"@angular/common": "~12.1.0-",
"@angular/compiler": "~12.1.0-",
"@angular/core": "~12.1.0-",
"@angular/forms": "~12.1.0-",
"@angular/platform-browser": "~12.1.0-",
"@angular/platform-browser-dynamic": "~12.1.0-",
"@angular/router": "~12.1.0-",
"bootstrap": "^5.0.2",
"jquery": "^3.6.0",
"rxjs": "~6.6.0",
"tslib": "^2.2.0",
"zone.js": "~0.11.4"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@angular-devkit/build-angular": "~12.1.3",
"@angular/cli": "~12.1.3",
"@angular/compiler-cli": "~12.1.0-",
"@types/jasmine": "~3.8.0",
"@types/node": "^12.11.1",
"jasmine-core": "~3.8.0",
"karma": "~6.3.0",
"karma-chrome-launcher": "~3.1.0",
"karma-coverage": "~2.0.3",
"karma-jasmine": "~4.0.0",
"karma-jasmine-html-reporter": "~1.7.0",
"typescript": "~4.3.2"
}
}13. App Routing Module
Path: /src/app/app.routing.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { EmployeeListComponent } from './employee-list/employee-list.component';
import { CreateEmployeeComponent } from './create-employee/create-employee.component';
import { UpdateEmployeeComponent } from './update-employee/update-employee.component';
import { EmployeeDetailsComponent } from './employee-details/employee-details.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{path: 'employees', component: EmployeeListComponent},
{path: 'create-employee', component: CreateEmployeeComponent},
{path: '', redirectTo: 'employees', pathMatch: 'full'},
{path: 'update-employee/:id', component: UpdateEmployeeComponent},
{path: 'employee-details/:id', component: EmployeeDetailsComponent}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }14. App Component
Path: /src/app/app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular + Spring Boot CRUD Full Stack App';
}15. App Component Template
Path: /src/app/app.component.html
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-sm bg-primary navbar-dark">
<ul class = "navbar-nav">
<li class = "nav-item">
<a routerLink="employees" routerLinkActive="active" class="nav-link" >Employee List</a>
</li>
<li class = "nav-item">
<a routerLink="create-employee" routerLinkActive="active" class="nav-link" >Add Employee</a>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
<h1 class="text-center"> {{title}} </h1>
<div class = "container">
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
<footer class = "footer">
<div class = "container">
<span>All Rights Reserved 2020 @JavaGuides</span>
</div>
</footer>16. App Module
Path: /src/app/app.module.ts
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http'
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { EmployeeListComponent } from './employee-list/employee-list.component';
import { CreateEmployeeComponent } from './create-employee/create-employee.component';
import { FormsModule} from '@angular/forms';
import { UpdateEmployeeComponent } from './update-employee/update-employee.component';
import { EmployeeDetailsComponent } from './employee-details/employee-details.component'
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
EmployeeListComponent,
CreateEmployeeComponent,
UpdateEmployeeComponent,
EmployeeDetailsComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
AppRoutingModule,
HttpClientModule,
FormsModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }17. Running Angular Client Application
ng serveng serve --port 4201



![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)

















Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment