In this tutorial, we will learn how to deploy the Spring boot WAR file on tomcat in AWS using the Elastic beanstalk service.
I have explained this tutorial in detail in my YouTube video so refer to my below YouTube video to implement this tutorial step by step.
We basically create a Spring boot project, package it as a WAR file, and deploy it in tomcat server on AWS cloud using Elastic beanstalk service.
What is AWS Elastic Beanstalk?
Development Process:
1. Create Spring Boot Application
2. Create Spring MVC Controller and Thymeleaf Page
3. Configure Spring boot as WAR
4. Package the WAR file using Maven
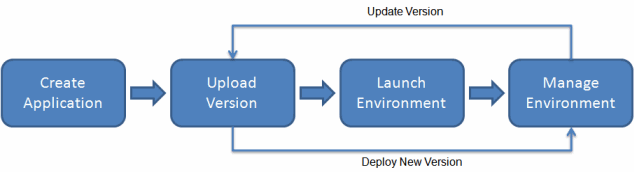
5. Create a new application in Elastic Beanstalk
6. Upload the WAR file to Elastic Beanstalk
#aws #springboot #javaguides
1. Create Spring Boot Application
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.4.3</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>net.javaguides</groupId> <artifactId>springboot-web-app-tomcat</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <name>springboot-web-app-tomcat</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>springboot-web-app-tomcat</finalName> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
2. Create Spring MVC Controller and Thymeleaf Page
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h1 th:text = "${message}"></h1> </body> </html>
Let's create a WelcomeController.java Spring MVC controller to return above Thymeleaf page:
package net.javaguides.springboot; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; @Controller public class WelcomeController { @GetMapping("/welcome") public String welcome(Model model) { model.addAttribute("message", "Deploying Spring Boot WAR file on tomcat in AWS"); return "welcome"; } }
3. Configure Spring boot as WAR
4. Package the WAR file using Maven
mvn clean install
5. Create a new application in Elastic Beanstalk
How to change the post?
server.port=5000
Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment