📘 Premium Read: Access my best content on Medium member-only articles — deep dives into Java, Spring Boot, Microservices, backend architecture, interview preparation, career advice, and industry-standard best practices.
🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (176K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
Use the below links to visit different parts of this tutorial:
- Spring Boot + Angular 10 CRUD Example Tutorial - Main Tutorial
- Spring Boot + Angular 10 CRUD Full Stack - Part 1 - Develop Spring Boot CRUD Rest APIs
- Spring Boot + Angular 10 CRUD Full Stack - Part 2 - Create an Angular 10 App
- Spring Boot + Angular 10 CRUD Full Stack - Part 3 - Develop Angular 10 CRUD Operations
- Spring Boot + Angular 10 CRUD Full Stack - Part 4 - Angular 10 CRUD App Configuration
- Spring Boot 2 + Angular 10 CRUD Full Stack - Part 5 - Running Angular 10 CRUD App
High-level architecture of Spring boot project
Spring Boot CRUD Rest APIs Development
This Spring Boot project is upgraded to Spring Boot 3 and Java 17.
1. Creating and Importing a Project
There are many ways to create a Spring Boot application. The simplest way is to use Spring Initializrat http://start.spring.io/, which is an online Spring Boot application generator.Go to http://start.spring.io website to create a Spring Boot project.Look at the above diagram, we have specified the following details:- Generate: Maven Project
- Java Version: 17 (Default)
- Spring Boot Version: keep default selected
- Group: net.guides.springboot2
- Artifact: springboot2-jpa-crud-example
- Name: springboot2-jpa-crud-example
- Description: Rest API for a Simple Employee Management Application
- Package Name : net.guides.springboot2.springboot2jpacrudexample
- Packaging: jar (This is the default value)
- Dependencies: Web, JPA, MySQL, DevTools
Once, all the details are entered, click on Generate Project button will generate a spring boot project and downloads it. Next, Unzip the downloaded zip file and import it into your favorite IDE.
- Generate: Maven Project
- Java Version: 17 (Default)
- Spring Boot Version: keep default selected
- Group: net.guides.springboot2
- Artifact: springboot2-jpa-crud-example
- Name: springboot2-jpa-crud-example
- Description: Rest API for a Simple Employee Management Application
- Package Name : net.guides.springboot2.springboot2jpacrudexample
- Packaging: jar (This is the default value)
- Dependencies: Web, JPA, MySQL, DevTools
2. Packaging Structure
Following is the packing structure of our Employee Management System -
3. The pom.xml File
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>net.guides.springboot2</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot2-jpa-crud-example</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>springboot2-jpa-crud-example</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project> <dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>4. MySQL Database Configuration
First, you need to create a database in MySQL server with the following command:create database EMS
create database EMS
Now, let's open the application.properties file in Spring boot project and add MySQL database details to connect to your MySQL database. Here is the application.properties file:
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/EMS?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username = root
spring.datasource.password = root
## Hibernate Properties
# The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen database
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
# Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, validate, update)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
server.servlet.context-path=/springboot-crud-rest
Make sure that you will change the above database configuration such as JDBC URL, username, and password as per your environment.
Hibernate will automatically create database tables so you only need to manually create the database and configure an application.properties file.
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/EMS?useSSL=false spring.datasource.username = root spring.datasource.password = root ## Hibernate Properties # The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen database spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect # Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, validate, update) spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update server.servlet.context-path=/springboot-crud-rest
5. Model Layer
- id - primary key
- firstName - First name of an employee
- lastName - Last name of an employee
- email - Email address of an employee
package net.guides.springboot2.springboot2jpacrudexample.model;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {
private long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String emailId;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String firstName, String lastName, String emailId) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.emailId = emailId;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(name = "first_name", nullable = false)
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
@Column(name = "last_name", nullable = false)
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@Column(name = "email_address", nullable = false)
public String getEmailId() {
return emailId;
}
public void setEmailId(String emailId) {
this.emailId = emailId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", emailId=" + emailId
+ "]";
}
}
6. Repository Layer
package net.guides.springboot2.springboot2jpacrudexample.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import net.guides.springboot2.springboot2jpacrudexample.model.Employee;
@Repository
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long>{
}
7. Controller Layer
package net.guides.springboot2.springboot2jpacrudexample.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import net.guides.springboot2.springboot2jpacrudexample.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import net.guides.springboot2.springboot2jpacrudexample.model.Employee;
import net.guides.springboot2.springboot2jpacrudexample.repository.EmployeeRepository;
@RestController @CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:4200")
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@GetMapping("/employees")
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees() {
return employeeRepository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/employees/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Employee> getEmployeeById(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId)
throws ResourceNotFoundException {
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(employee);
}
@PostMapping("/employees")
public Employee createEmployee(@Valid @RequestBody Employee employee) {
return employeeRepository.save(employee);
}
@PutMapping("/employees/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Employee> updateEmployee(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId,
@Valid @RequestBody Employee employeeDetails) throws ResourceNotFoundException {
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));
employee.setEmailId(employeeDetails.getEmailId());
employee.setLastName(employeeDetails.getLastName());
employee.setFirstName(employeeDetails.getFirstName());
final Employee updatedEmployee = employeeRepository.save(employee);
return ResponseEntity.ok(updatedEmployee);
}
@DeleteMapping("/employees/{id}")
public Map<String, Boolean> deleteEmployee(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId)
throws ResourceNotFoundException {
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));
employeeRepository.delete(employee);
Map<String, Boolean> response = new HashMap<>();
response.put("deleted", Boolean.TRUE);
return response;
}
}
Enable CORS on the Server
To enable CORS on the server, add a @CrossOrigin annotation to the EmployeeController
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:4200")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
public class EmployeeController {
// ....
}
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:4200")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
public class EmployeeController {
// ....
}
8. Exception(Error) Handling for RESTful Services
Resource Not Present
{
"timestamp": 1512713804164,
"status": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"message": "No message available",
"path": "/some-dummy-url"
}
What happens when we throw an Exception?
package com.companyname.springbootcrudrest.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class ResourceNotFoundException extends Exception{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public ResourceNotFoundException(String message){
super(message);
}
}
Customizing Error Response Structure
package com.companyname.springbootcrudrest.exception;
import java.util.Date;
public class ErrorDetails {
private Date timestamp;
private String message;
private String details;
public ErrorDetails(Date timestamp, String message, String details) {
super();
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.message = message;
this.details = details;
}
public Date getTimestamp() {
return timestamp;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public String getDetails() {
return details;
}
}
package com.companyname.springbootcrudrest.exception;
import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> resourceNotFoundException(ResourceNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) {
ErrorDetails errorDetails = new ErrorDetails(new Date(), ex.getMessage(), request.getDescription(false));
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorDetails, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> globleExcpetionHandler(Exception ex, WebRequest request) {
ErrorDetails errorDetails = new ErrorDetails(new Date(), ex.getMessage(), request.getDescription(false));
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorDetails, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
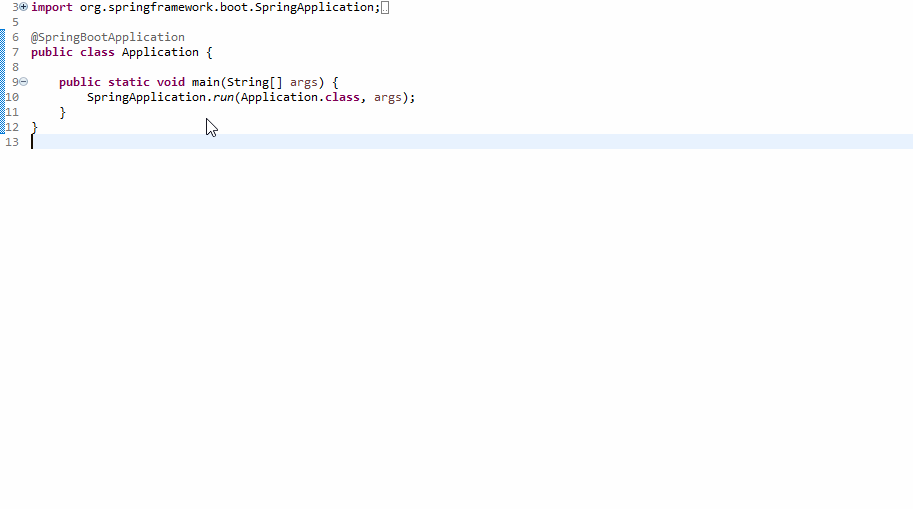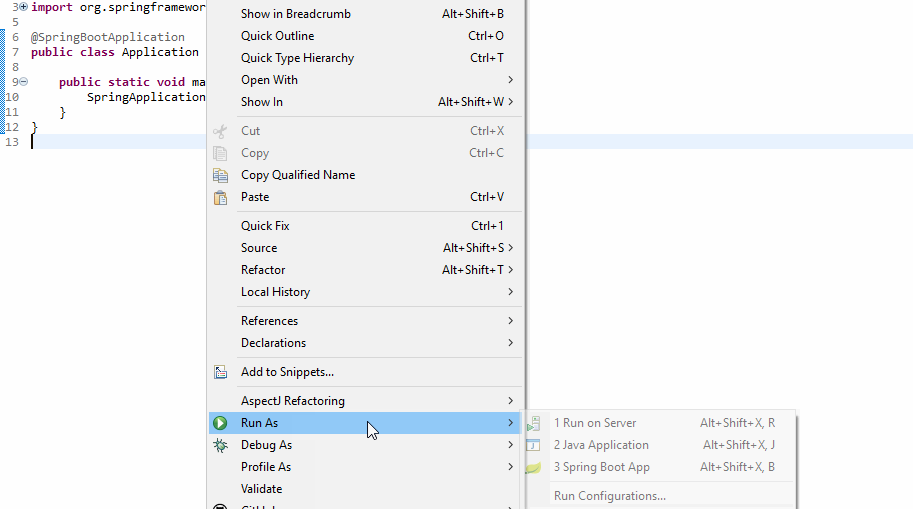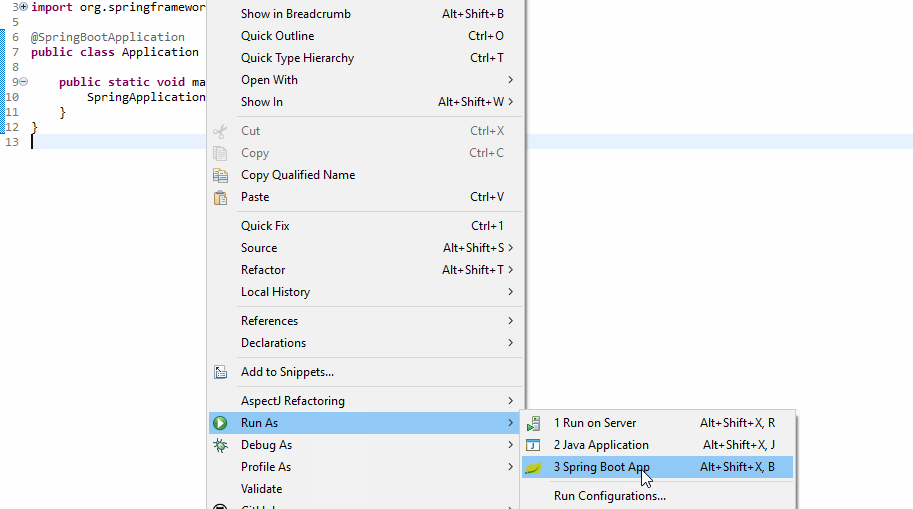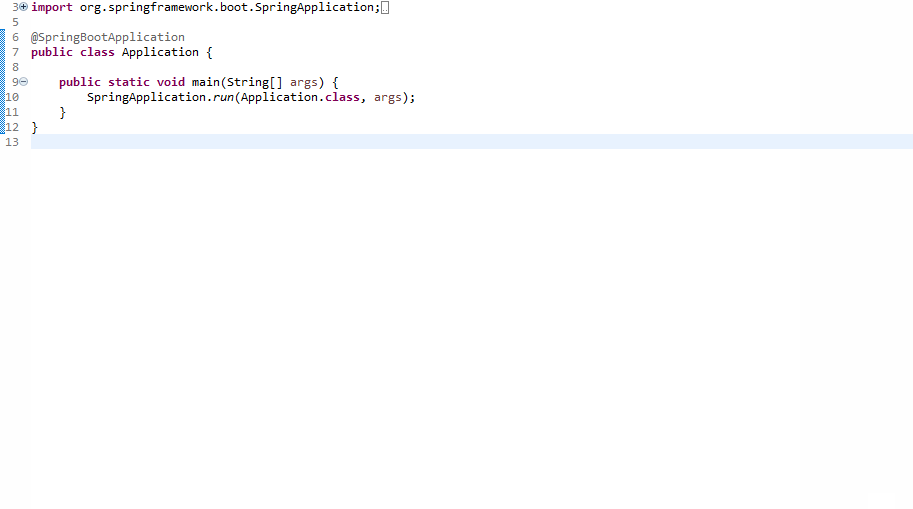
9. Running Application
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
$ mvn spring-boot:runGitHub Link
You can download the source code of this spring boot project from GitHub repository at https://github.com/RameshMF/Angular10-SpringBoot-CRUD-Tutorial
Move to Part 2 - Create an Angular 10 CRUD App
- Install the latest version of Angular CLI
- Create Angular 10 client application using Angular CLI
- Identify Components, Services, and Modules
- Create Service & Components using Angular CLI
- Integrate JQuery and Bootstrap with Angular




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)













Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment