📘 Premium Read: Access my best content on Medium member-only articles — deep dives into Java, Spring Boot, Microservices, backend architecture, interview preparation, career advice, and industry-standard best practices.
🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (176K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
Learn spring boot at https://www.javaguides.net/p/spring-boot-tutorial.html.
Learn Hibernate at https://www.javaguides.net/p/hibernate-tutorial.html
Learn Spring Data JPA at https://www.javaguides.net/p/spring-data-jpa-tutorial.html
Video Tutorial
Project Requirements
- Get all the employees
- Add a new employee
- Update an employee
- Delete an employee
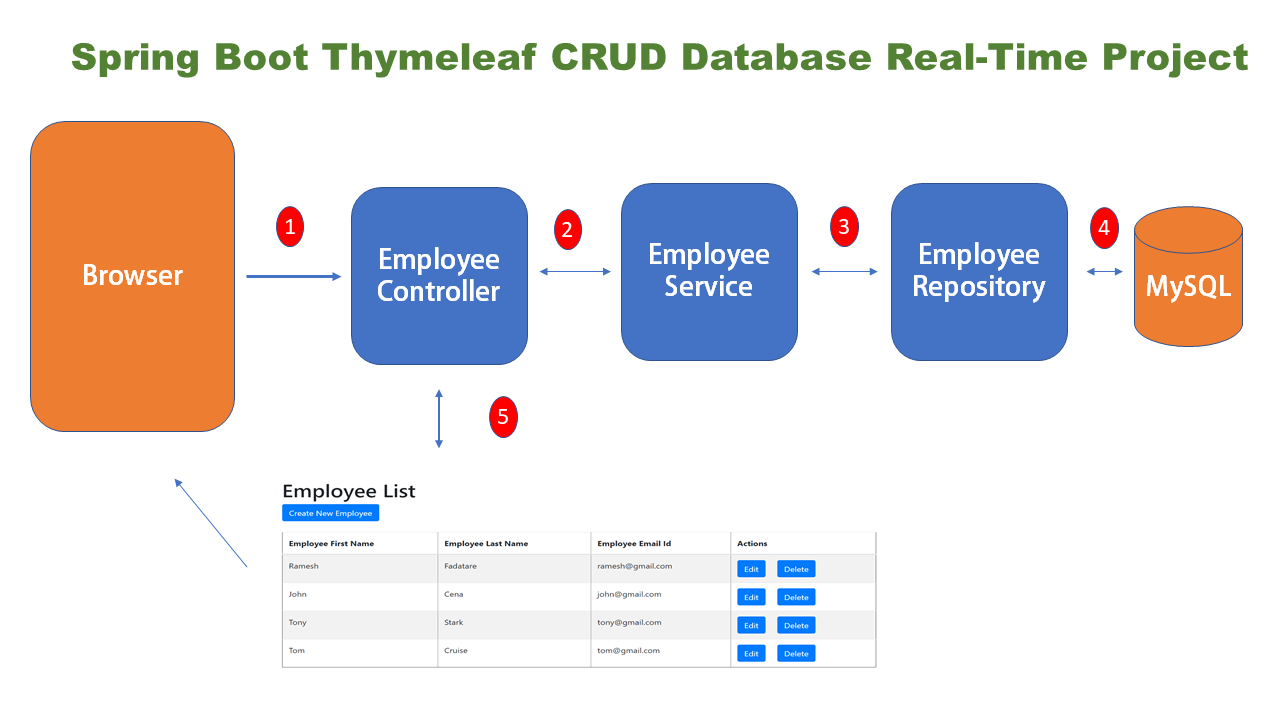
What we will build?
Application Flow
Tools and technologies used
- IDE - Eclipse / STS
- Spring Boot 3+
- Spring Framework 6+
- Maven
- Java 17
- Spring Data JPA ( Hibernate)
- Thymeleaf
1. Create Spring Boot Project
2. Maven Dependencies
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
3. Project Structure
4. Configure and Setup MySQL Database
# DATASOURCE (DataSourceAutoConfiguration & DataSourceProperties)
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
# Hibernate
# The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen database
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
# Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, validate, update)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
logging.level.org.hibernate.SQL=DEBUG
logging.level.org.hibernate.type=TRACE
5. Model Layer - Create JPA Entity - Employee.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.model;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email")
private String email;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
6. Repository Layer - EmployeeRepository.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
@Repository
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long>{
}
7. Service Layer
7.1 EmployeeService.java interface
package net.javaguides.springboot.service;
import java.util.List;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
public interface EmployeeService {
List < Employee > getAllEmployees();
void saveEmployee(Employee employee);
Employee getEmployeeById(long id);
void deleteEmployeeById(long id);
}
7.2. EmployeeServiceImpl class
package net.javaguides.springboot.service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.EmployeeRepository;
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService {
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@Override
public List < Employee > getAllEmployees() {
return employeeRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public void saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
this.employeeRepository.save(employee);
}
@Override
public Employee getEmployeeById(long id) {
Optional < Employee > optional = employeeRepository.findById(id);
Employee employee = null;
if (optional.isPresent()) {
employee = optional.get();
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(" Employee not found for id :: " + id);
}
return employee;
}
@Override
public void deleteEmployeeById(long id) {
this.employeeRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
8. Controller Layer - EmployeeController.java
package net.javaguides.springboot.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
import net.javaguides.springboot.service.EmployeeService;
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
// display list of employees
@GetMapping("/")
public String viewHomePage(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("listEmployees", employeeService.getAllEmployees());
return "index";
}
@GetMapping("/showNewEmployeeForm")
public String showNewEmployeeForm(Model model) {
// create model attribute to bind form data
Employee employee = new Employee();
model.addAttribute("employee", employee);
return "new_employee";
}
@PostMapping("/saveEmployee")
public String saveEmployee(@ModelAttribute("employee") Employee employee) {
// save employee to database
employeeService.saveEmployee(employee);
return "redirect:/";
}
@GetMapping("/showFormForUpdate/{id}")
public String showFormForUpdate(@PathVariable(value = "id") long id, Model model) {
// get employee from the service
Employee employee = employeeService.getEmployeeById(id);
// set employee as a model attribute to pre-populate the form
model.addAttribute("employee", employee);
return "update_employee";
}
@GetMapping("/deleteEmployee/{id}")
public String deleteEmployee(@PathVariable(value = "id") long id) {
// call delete employee method
this.employeeService.deleteEmployeeById(id);
return "redirect:/";
}
}
9. View Layer
9.1 index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1"> <title>Employee Management System</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.3/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-MCw98/SFnGE8fJT3GXwEOngsV7Zt27NXFoaoApmYm81iuXoPkFOJwJ8ERdknLPMO" crossorigin="anonymous"> </head> <body> <div class="container my-2"> <h1>Employees List</h1> <a th:href="@{/showNewEmployeeForm}" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm mb-3"> Add Employee </a> <table border="1" class="table table-striped table-responsive-md"> <thead> <tr> <th>Employee First Name</th> <th>Employee Last Name</th> <th>Employee Email</th> <th> Actions </th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr th:each="employee : ${listEmployees}"> <td th:text="${employee.firstName}"></td> <td th:text="${employee.lastName}"></td> <td th:text="${employee.email}"></td> <td> <a th:href="@{/showFormForUpdate/{id}(id=${employee.id})}" class="btn btn-primary">Update</a> <a th:href="@{/deleteEmployee/{id}(id=${employee.id})}" class="btn btn-danger">Delete</a> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div> </body> </html>
9.2 new_employee.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1"> <title>Employee Management System</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.3/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-MCw98/SFnGE8fJT3GXwEOngsV7Zt27NXFoaoApmYm81iuXoPkFOJwJ8ERdknLPMO" crossorigin="anonymous"> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <h1>Employee Management System</h1> <hr> <h2>Save Employee</h2> <form action="#" th:action="@{/saveEmployee}" th:object="${employee}" method="POST"> <input type="text" th:field="*{firstName}" placeholder="Employee First Name" class="form-control mb-4 col-4"> <input type="text" th:field="*{lastName}" placeholder="Employee Last Name" class="form-control mb-4 col-4"> <input type="text" th:field="*{email}" placeholder="Employee Email" class="form-control mb-4 col-4"> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-info col-2"> Save Employee</button> </form> <hr> <a th:href="@{/}"> Back to Employee List</a> </div> </body> </html>
9.3 update_employee.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<title>Employee Management System</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.3/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-MCw98/SFnGE8fJT3GXwEOngsV7Zt27NXFoaoApmYm81iuXoPkFOJwJ8ERdknLPMO" crossorigin="anonymous">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>Employee Management System</h1>
<hr>
<h2>Update Employee</h2>
<form action="#" th:action="@{/saveEmployee}" th:object="${employee}" method="POST">
<!-- Add hidden form field to handle update -->
<input type="hidden" th:field="*{id}" />
<input type="text" th:field="*{firstName}" class="form-control mb-4 col-4">
<input type="text" th:field="*{lastName}" class="form-control mb-4 col-4">
<input type="text" th:field="*{email}" class="form-control mb-4 col-4">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-info col-2"> Update Employee</button>
</form>
<hr>
<a th:href="@{/}"> Back to Employee List</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
10. Run Spring application and demo
$ mvn spring-boot:runDemo
List Employees Page
Update Employee Page
Add Employee Page
GitHub Repository Link
You can download/clone source code of this tutorial from my GitHub repository at https://github.com/RameshMF/springboot-thymeleaf-crud-pagination-sorting-webapp.git
Further Readings
Pagination and Sorting with Spring Boot, ThymeLeaf, Spring Data JPA, Hibernate, MySQL




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)














Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment