📘 Premium Read: Access my best content on Medium member-only articles — deep dives into Java, Spring Boot, Microservices, backend architecture, interview preparation, career advice, and industry-standard best practices.
🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (176K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
🚀 Introduction to Java Supplier Functional Interface
In Java functional programming, the Supplier<T> interface (from java.util.function) is a functional interface that takes no input but returns a result when called.
✅ T (Return Type): The type of value that the Supplier provides.
✅ Common Use Cases:
✔ Generating dynamic values – Timestamps, random numbers, unique IDs.
✔ Lazy initialization – Creating objects only when needed.
✔ Providing default configurations – Supplying fallback values when required.
📌 In this article, you’ll learn:
✅ How to use Supplier<T> with examples.
✅ How to use get() for retrieving values on demand.
✅ Real-world use cases where Supplier improves Java applications.
1️⃣ Using get() to Return Values
The get() method retrieves a value from the Supplier whenever it is called.
✔ Example: Returning a Constant Value
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class SupplierGetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ✅ Define a Supplier that returns a constant value
Supplier<String> constantSupplier = () -> "Hello World!";
String result = constantSupplier.get();
System.out.println(result); // Output: Hello World!
}
}📌 Why use Supplier here?
✅ Encapsulates logic inside a function.
✅ Provides flexibility to return values dynamically.
🚀 Use Supplier<T> for functions that return values without input!
2️⃣ Generating Dynamic Data with Supplier
✔ Example: Returning the Current Date and Time
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class SupplierGetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ✅ Supplier that returns the current date and time
Supplier<LocalDateTime> dateTimeSupplier = () -> LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime currentDateTime = dateTimeSupplier.get();
System.out.println(currentDateTime);
}
}📌 Why use Supplier for timestamps?
✅ Generates values dynamically at runtime.
✅ Eliminates the need for unnecessary parameters.
🚀 Use Supplier when retrieving dynamic values like timestamps!
3️⃣ Using Supplier for Default Configurations
✔ Example: Providing a Default Configuration
import java.util.function.Supplier;
class Configuration {
private String url;
private int timeout;
public Configuration(String url, int timeout) {
this.url = url;
this.timeout = timeout;
}
public String getUrl() { return url; }
public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; }
public int getTimeout() { return timeout; }
public void setTimeout(int timeout) { this.timeout = timeout; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Configuration{" +
"url='" + url + '\'' +
", timeout=" + timeout +
'}';
}
}
public class DefaultConfigurationSupplierExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ✅ Supplier that provides a default configuration
Supplier<Configuration> defaultConfiguration =
() -> new Configuration("http://localhost:8080", 50000);
Configuration configuration = defaultConfiguration.get();
System.out.println(configuration.toString());
}
}📌 Why use Supplier for configuration loading?
✅ Lazy initialization – The configuration object is created only when needed.
✅ Provides default settings – Ensures fallback values when necessary.
🚀 Use Supplier for loading default configurations efficiently!
4️⃣ Real-World Use Cases of Supplier Interface
✔ Use Case 1: Lazy Loading Data from a Database
Fetching user data from a database only when required.
import java.util.function.Supplier;
class Database {
public static String fetchUserData() {
System.out.println("Fetching user data from database...");
return "User: Ramesh, Age: 30";
}
}
public class LazyLoadingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ✅ Supplier for lazy database access
Supplier<String> userDataSupplier = () -> Database.fetchUserData();
System.out.println("Before accessing data...");
// User data is fetched only when get() is called
System.out.println(userDataSupplier.get());
}
}📌 Why use Supplier for database operations?
✅ Delays expensive operations until they are needed.
✅ Improves performance by avoiding unnecessary calls.
🚀 Use Supplier to optimize expensive operations like database access!
✔ Use Case 2: Generating Random OTP (One-Time Password)
import java.util.function.Supplier;
import java.util.Random;
public class OTPGenerator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ✅ Supplier to generate a 6-digit OTP
Supplier<String> otpSupplier = () -> {
Random random = new Random();
return String.format("%06d", random.nextInt(1000000));
};
System.out.println("Generated OTP: " + otpSupplier.get());
}
}📌 Why use Supplier for OTP generation?
✅ Ensures a new OTP is generated every time get() is called.
✅ Encapsulates logic into a reusable function.
🚀 Use Supplier for generating dynamic security codes like OTPs!
🔥 Best Practices for Using Supplier Functional Interface
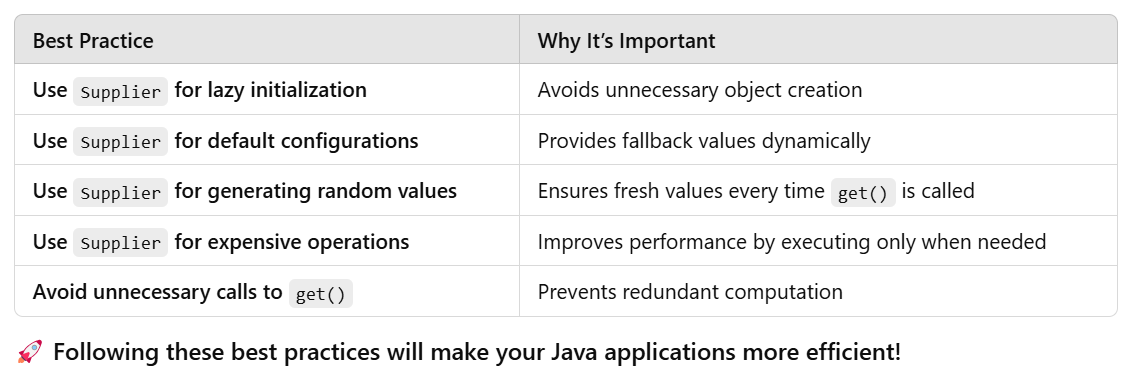
Supplier Functional Interface🔑 Key Takeaways
✅ The Supplier<T> interface generates values dynamically.
✅ Use get() to retrieve values on demand.
✅ Use Supplier for lazy initialization and default configurations.
✅ Apply Supplier in real-world cases like database access, OTP generation, and timestamps.
By mastering the Supplier functional interface, your Java code will be more efficient, modular, and optimized! 🚀




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)










Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment