Registration and Login using Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring Data JPA, Hibernate, H2, JSP and Bootstrap
In this tutorial, we will learn step by step how to create a User Account Registration and Login module using Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring Data JPA, Hibernate, H2, JSP, and Bootstrap.
Learn Spring Boot in-depth on Spring Boot TutorialLearn Spring Boot Login and Registration REST API at Login and Registration REST API using Spring Boot, Spring Security, Hibernate, and MySQL Database
You can download the source code of this tutorial from my GitHub repository (link provided at the end of this tutorial).
Tools and Technologies Used
- Spring Boot
- JDK - 1.8 or later
- Hibernate
- Maven
- Spring Data JPA
- IDE - Eclipse or Spring Tool Suite (STS)
- MYSQL
- Spring Security
- JSP
1. Creating a Spring Boot Application
There are many ways to create a Spring Boot application. You can refer to the below articles to create a Spring Boot application.
>> Create Spring Boot Project With Spring Initializer
>> Create Spring Boot Project in Spring Tool Suite [STS]
>> Create Spring Boot Project in Spring Tool Suite [STS]
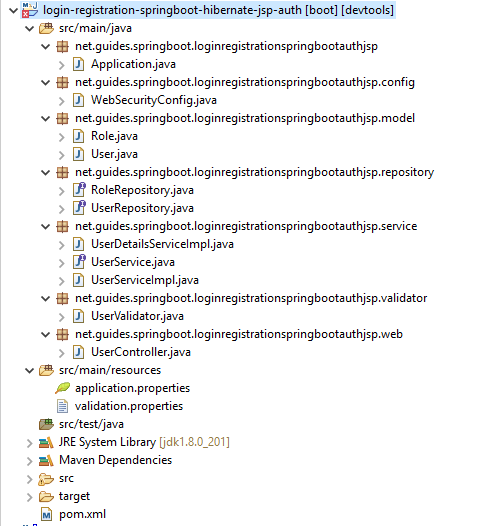
Refer to the next step to create a project packaging structure.
3. The pom.xml File
Here is the pom.xml file for your reference:
<project
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>springboot.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>login-registration-springboot-hibernate-jsp-auth</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>login-registration-springboot-hibernate-jsp-auth Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath />
<!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>bootstrap</artifactId>
<version>3.3.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>bootstrap-datepicker</artifactId>
<version>1.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>1.9.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
4. Domain or Model Layer
In this step, we will create User and Role JPA entities and establish MANY-to-MANY relationships between them.Let's use JPA annotations to establish MANY-to-MANY relationships between User and Role entities.
User JPA Entity
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.Set;
@Entity
@Table(name = "user")
public class User {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String passwordConfirm;
private Set < Role > roles;
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Transient
public String getPasswordConfirm() {
return passwordConfirm;
}
public void setPasswordConfirm(String passwordConfirm) {
this.passwordConfirm = passwordConfirm;
}
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(name = "user_role", joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "user_id"), inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "role_id"))
public Set < Role > getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(Set < Role > roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
}
Role JPA Entity
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.Set;
@Entity
@Table(name = "role")
public class Role {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Set < User > users;
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@ManyToMany(mappedBy = "roles")
public Set < User > getUsers() {
return users;
}
public void setUsers(Set < User > users) {
this.users = users;
}
}
- @Table maps the entity with the table. If no @Table is defined, the default value is used: the class name of the entity.
- @Id declares the identifier property of the entity.
- @ManyToMany defines a many-to-many relationship between 2 entities.
- mappedBy indicates the entity is the inverse of the relationship.
5. Repository Layer
Let's create a UserRepository to access the User's data from the database.
Well, Spring Data JPA comes with a JpaRepository interface that defines methods for all the CRUD operations on the entity, and a default implementation of JpaRepository called SimpleJpaRepository.
UserRepository.java
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import net.guides.springboot.loginregistrationspringbootauthjsp.model.User;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
User findByUsername(String username);
}
RoleRepository.java
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import net.guides.springboot.loginregistrationspringbootauthjsp.model.Role;
public interface RoleRepository extends JpaRepository<Role, Long>{
}
6. Service Layer
UserDetailsServiceImpl.java
To implement login/authentication with Spring Security, we need to implement org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService interface and load User details from database.import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import net.guides.springboot.loginregistrationspringbootauthjsp.model.Role;
import net.guides.springboot.loginregistrationspringbootauthjsp.model.User;
import net.guides.springboot.loginregistrationspringbootauthjsp.repository.UserRepository;
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userRepository.findByUsername(username);
Set < GrantedAuthority > grantedAuthorities = new HashSet < > ();
for (Role role: user.getRoles()) {
grantedAuthorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role.getName()));
}
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), grantedAuthorities);
}
}
UserService.java
import net.guides.springboot.loginregistrationspringbootauthjsp.model.User;
public interface UserService {
void save(User user);
User findByUsername(String username);
}
UserServiceImpl.java
import java.util.HashSet; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import net.guides.springboot.loginregistrationspringbootauthjsp.model.User; import net.guides.springboot.loginregistrationspringbootauthjsp.repository.RoleRepository; import net.guides.springboot.loginregistrationspringbootauthjsp.repository.UserRepository; @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Autowired private UserRepository userRepository; @Autowired private RoleRepository roleRepository; @Autowired private BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder; @Override public void save(User user) { user.setPassword(bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode(user.getPassword())); user.setRoles(new HashSet < > (roleRepository.findAll())); userRepository.save(user); } @Override public User findByUsername(String username) { return userRepository.findByUsername(username); } }
7. Spring Validator
To provide input-data validation for /registration controller with Spring Validator, we implement org.springframework.validation.Validator:UserValidator.java
import com.hellokoding.auth.model.User;
import com.hellokoding.auth.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.validation.Errors;
import org.springframework.validation.ValidationUtils;
import org.springframework.validation.Validator;
@Component
public class UserValidator implements Validator {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> aClass) {
return User.class.equals(aClass);
}
@Override
public void validate(Object o, Errors errors) {
User user = (User) o;
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "username", "NotEmpty");
if (user.getUsername().length() < 6 || user.getUsername().length() > 32) {
errors.rejectValue("username", "Size.userForm.username");
}
if (userService.findByUsername(user.getUsername()) != null) {
errors.rejectValue("username", "Duplicate.userForm.username");
}
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmptyOrWhitespace(errors, "password", "NotEmpty");
if (user.getPassword().length() < 8 || user.getPassword().length() > 32) {
errors.rejectValue("password", "Size.userForm.password");
}
if (!user.getPasswordConfirm().equals(user.getPassword())) {
errors.rejectValue("passwordConfirm", "Diff.userForm.passwordConfirm");
}
}
}
8. Controller Layer
The controller layer acts as an interface between View and Model. It receives requests from the View layer and processes them, including the necessary validations.
UserController.java
Let's create Spring MVC controller - UserController with the following method handlers to handle the request and return view:
import com.hellokoding.auth.model.User;
import com.hellokoding.auth.service.UserService;
import com.hellokoding.auth.validator.UserValidator;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private UserValidator userValidator;
@GetMapping("/registration")
public String registration(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("userForm", new User());
return "registration";
}
@PostMapping("/registration")
public String registration(@ModelAttribute("userForm") User userForm, BindingResult bindingResult) {
userValidator.validate(userForm, bindingResult);
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
return "registration";
}
userService.save(userForm);
return "redirect:/welcome";
}
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login(Model model, String error, String logout) {
if (error != null)
model.addAttribute("error", "Your username and password is invalid.");
if (logout != null)
model.addAttribute("message", "You have been logged out successfully.");
return "login";
}
@GetMapping({"/", "/welcome"})
public String welcome(Model model) {
return "welcome";
}
}
9. View Layer
This layer represents the output of the application, usually some form of UI. The presentation layer is used to display the Model data fetched by the Controller.
We are using JSP as the view layer in this example.
registration.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<c:set var="contextPath" value="${pageContext.request.contextPath}"/>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Create an account</title>
<link href="${contextPath}/resources/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="${contextPath}/resources/css/common.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<form:form method="POST" modelAttribute="userForm" class="form-signin">
<h2 class="form-signin-heading">Create your account</h2>
<spring:bind path="username">
<div class="form-group ${status.error ? 'has-error' : ''}">
<form:input type="text" path="username" class="form-control" placeholder="Username"
autofocus="true"></form:input>
<form:errors path="username"></form:errors>
</div>
</spring:bind>
<spring:bind path="password">
<div class="form-group ${status.error ? 'has-error' : ''}">
<form:input type="password" path="password" class="form-control" placeholder="Password"></form:input>
<form:errors path="password"></form:errors>
</div>
</spring:bind>
<spring:bind path="passwordConfirm">
<div class="form-group ${status.error ? 'has-error' : ''}">
<form:input type="password" path="passwordConfirm" class="form-control"
placeholder="Confirm your password"></form:input>
<form:errors path="passwordConfirm"></form:errors>
</div>
</spring:bind>
<button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit">Submit</button>
</form:form>
</div>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.11.2/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="${contextPath}/resources/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
login.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<c:set var="contextPath" value="${pageContext.request.contextPath}"/>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Log in with your account</title>
<link href="${contextPath}/resources/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="${contextPath}/resources/css/common.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<form method="POST" action="${contextPath}/login" class="form-signin">
<h2 class="form-heading">Log in</h2>
<div class="form-group ${error != null ? 'has-error' : ''}">
<span>${message}</span>
<input name="username" type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Username"
autofocus="true"/>
<input name="password" type="password" class="form-control" placeholder="Password"/>
<span>${error}</span>
<input type="hidden" name="${_csrf.parameterName}" value="${_csrf.token}"/>
<button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit">Log In</button>
<h4 class="text-center"><a href="${contextPath}/registration">Create an account</a></h4>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.11.2/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="${contextPath}/resources/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
welcome.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<c:set var="contextPath" value="${pageContext.request.contextPath}"/>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Create an account</title>
<link href="${contextPath}/resources/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<c:if test="${pageContext.request.userPrincipal.name != null}">
<form id="logoutForm" method="POST" action="${contextPath}/logout">
<input type="hidden" name="${_csrf.parameterName}" value="${_csrf.token}"/>
</form>
<h2>Welcome ${pageContext.request.userPrincipal.name} | <a onclick="document.forms['logoutForm'].submit()">Logout</a></h2>
</c:if>
</div>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.11.2/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="${contextPath}/resources/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
10. Configure Properties File
Configure JSP View Resolver
## Spring view resolver set up
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/WEB-INF/jsp/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
Configure MySQL database
Since we’re using MySQL as our database, we need to configure the database URL, username, and password so that Spring can establish a connection with the database on startup. Open src/main/resources/application.properties file and add the following properties to it:spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=Mysql@123
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
You don’t need to create any tables. The tables will automatically be created by Hibernate from the Employee entity that we will define in the next step. This is made possible by the property spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update.
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=Mysql@123
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = updateYou don’t need to create any tables. The tables will automatically be created by Hibernate from the Employee entity that we will define in the next step. This is made possible by the property spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update.
Validation.properties file
Create validation.properties file under resource folder and add the following content to it:
NotEmpty=This field is required.
Size.userForm.username=Please use between 6 and 32 characters.
Duplicate.userForm.username=Someone already has that username.
Size.userForm.password=Try one with at least 8 characters.
Diff.userForm.passwordConfirm=These passwords don't match.
11. Web Security Configuration
WebSecurityConfig.java
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/resources/**", "/registration").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.permitAll();
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager customAuthenticationManager() throws Exception {
return authenticationManager();
}
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(bCryptPasswordEncoder());
}
}
12. Run Application
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
13. Demo
Registration Page
Registration Page Validation
Login Page
Logout Page
14. Source Code on GitHub Repository
The source code of this tutorial is available on my GitHub repository at login-registration-spring-boot-hibernate-jsp-auth.





what does the role do?? it is like an administrator?? or what
ReplyDeletegood , thanks bro !!
ReplyDeletewhere is SecurityService comes from?
ReplyDeleteSecurityService will not come in controller please fix the code
ReplyDeleteFixed. Thanks for reporting!.
DeleteHow can i download this github project ??
ReplyDeleteSirji, iska video tutorial hai kya ?
ReplyDelete