In this article, you’ll learn how to configure Spring Boot, and Spring Data JPA to use the Microsoft SQL Server database and build a Restful CRUD API for Employee Management System.
Spring makes switching between RDBMs simple. When you’re using Spring Data JPA with an ORM technology such as Hibernate, the persistence layer is nicely well-decoupled. As we are using Hibernate so it will support out of the box to work with different database vendors without changing the underlying code.
Follow these quick three steps to configure the Microsoft SQL server in the Spring boot application with Spring Data JPA:
Spring makes switching between RDBMs simple. When you’re using Spring Data JPA with an ORM technology such as Hibernate, the persistence layer is nicely well-decoupled. As we are using Hibernate so it will support out of the box to work with different database vendors without changing the underlying code.
Follow these quick three steps to configure the Microsoft SQL server in the Spring boot application with Spring Data JPA:
Step 1: Add Spring Data JPA Dependency
Let's use Spring Data JPA with the below dependency:
That's all. Now you are good to go.
Let's develop a complete CRUD RESTFul API for a Simple Employee Management System using Spring Boot, Spring Data JPA, and Microsoft SQL database.
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency>
Step 2: SQL Server Dependency
To connect with SQL Server from Java applications, Microsoft provides a Microsoft JDBC Driver for SQL Server. However, until November 2016, Maven did not directly support the driver as it was not open source. By making it open-source, Microsoft finally made the driver available on the Maven Central Repository. More information can be found here.
Add below MS-SQL JDBC driver dependency in your pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.sqlserver</groupId>
<artifactId>mssql-jdbc</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>Step 3: Configure the MS-SQL Server in an application.properties file
Configure Spring Boot to use an MS-SQL server database as our data source. We are simply add the Microsoft SQL server URL, username, and password in the src/main/resources/application.properties file:
spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:sqlserver://localhost;databaseName=employees spring.datasource.username=sa spring.datasource.password= spring.jpa.show-sql=true spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql = true ## Hibernate Properties # The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen database spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServer2012Dialect # Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, validate, update) spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
That's all. Now you are good to go.
Table of Contents
- What we’ll build?
- Tools and Technologies Used
- Creating and Importing a Project
- The pom.xml File
- Packaging Structure
- Configuring MS-SQL Server Database
- Create JPA Entity - Employee.java
- Create Spring Data Repository - EmployeeRepository.java
- Create Spring Rest Controller - EmployeeController.java
- Exception(Error) Handling for RESTful Services
- Running Application
- Integration Testing for REST APIs
- Testing REST APIs via Postman Client
- Source code on GitHub Repository
1. What we’ll build
We will build CRUD RESTFul APIs for a Simple Employee Management System using Spring Boot, Spring Data JPA, and MS-SQL database.
2. Tools and Technologies Used
- Spring Boot - 3+
- JDK - 17 or later
- Spring Framework - 6+
- Hibernate - 6+
- JPA
- Maven - 3.2+
- IDE - Eclipse or Spring Tool Suite (STS)
- Microsoft SQL Server - 4.0
3. Creating and Importing a Project
There are many ways to create a Spring Boot application. The simplest way is to use Spring Initializr, which is an online Spring Boot application generator.
Look at the above diagram, we have specified the following details:
- Generate: Maven Project
- Java Version: 17 (Default)
- Spring Boot:3.0.4
- Group: net.javaguides.mssq
- Artifact: springboot-mssql-jpa-hibernate-crud-example
- Name: springboot-mssql-jpa-hibernate-crud-example
- Description: springboot-mssql-jpa-hibernate-crud-example
- Package Name : net.javaguides.mssql
- Packaging: jar (This is the default value)
- Dependencies: Spring Web, Spring Data JPA
Once, all the details are entered, next, click on Generate Project button will generate a spring boot project and downloads it. Next, Unzip the downloaded zip file and import it into your favorite IDE.
4. Maven Dependencies
Make sure that you have the following Maven dependencies in your Spring Boot project:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.sqlserver</groupId>
<artifactId>mssql-jdbc</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>5. Packaging Structure
Let’s configure Spring Boot to use the Microsoft SQL server as our data source. You can do that simply by adding the Microsoft SQL database URL, username, and password in the src/main/resources/application.properties file -
spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:sqlserver://localhost;databaseName=employees spring.datasource.username=sa spring.datasource.password= spring.jpa.show-sql=true spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql = true ## Hibernate Properties # The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen database spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServer2012Dialect # Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, validate, update) spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
7. Create JPA Entity - Employee.java
Let's create an Employee JPA entity and add the following code to it:
package net.javaguides.mssql.model;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
@Column(name = "first_name", nullable = false)
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name", nullable = false)
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email_address", nullable = false)
private String emailId;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String firstName, String lastName, String emailId) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.emailId = emailId;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmailId() {
return emailId;
}
public void setEmailId(String emailId) {
this.emailId = emailId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", emailId=" + emailId
+ "]";
}
}8. Create Spring Data Repository - EmployeeRepository.java
package net.javaguides.mssql.repository;
import net.javaguides.mssql.model.Employee;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long>{
}9. Exception(Error) Handling for RESTful Services
Spring Boot provides a good default implementation for exception handling for RESTful Services. Let’s quickly look at the default Exception Handling features provided by Spring Boot.Let's create a ResourceNotFoundException.java class with the following code:package net.guides.springboot2.crud.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class ResourceNotFoundException extends Exception{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public ResourceNotFoundException(String message){
super(message);
}
}
Let’s define an ErrorDetails response bean with the following code:import java.util.Date;
public class ErrorDetails {
private Date timestamp;
private String message;
private String details;
public ErrorDetails(Date timestamp, String message, String details) {
super();
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.message = message;
this.details = details;
}
public Date getTimestamp() {
return timestamp;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public String getDetails() {
return details;
}
}
To use ErrorDetails to return the error response, let’s create a GlobalExceptionHandler class annotated with @ControllerAdvice annotation. This class handles exception-specific and global exceptions in a single place.import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> resourceNotFoundException(ResourceNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) {
ErrorDetails errorDetails = new ErrorDetails(new Date(), ex.getMessage(), request.getDescription(false));
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorDetails, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> globleExcpetionHandler(Exception ex, WebRequest request) {
ErrorDetails errorDetails = new ErrorDetails(new Date(), ex.getMessage(), request.getDescription(false));
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorDetails, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
Spring Boot provides a good default implementation for exception handling for RESTful Services. Let’s quickly look at the default Exception Handling features provided by Spring Boot.
Let's create a ResourceNotFoundException.java class with the following code:
package net.guides.springboot2.crud.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class ResourceNotFoundException extends Exception{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public ResourceNotFoundException(String message){
super(message);
}
}Let’s define an ErrorDetails response bean with the following code:
import java.util.Date;
public class ErrorDetails {
private Date timestamp;
private String message;
private String details;
public ErrorDetails(Date timestamp, String message, String details) {
super();
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.message = message;
this.details = details;
}
public Date getTimestamp() {
return timestamp;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public String getDetails() {
return details;
}
}To use ErrorDetails to return the error response, let’s create a GlobalExceptionHandler class annotated with @ControllerAdvice annotation. This class handles exception-specific and global exceptions in a single place.
import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> resourceNotFoundException(ResourceNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) {
ErrorDetails errorDetails = new ErrorDetails(new Date(), ex.getMessage(), request.getDescription(false));
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorDetails, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> globleExcpetionHandler(Exception ex, WebRequest request) {
ErrorDetails errorDetails = new ErrorDetails(new Date(), ex.getMessage(), request.getDescription(false));
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorDetails, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}10. Create Spring Rest Controller - EmployeeController.java
Let's create an EmployeeController Spring MVC controller and build CRUD REST APIs:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import jakarta.validation.Valid;
import net.javaguides.mssql.model.Employee;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import net.javaguides.mssql.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import net.javaguides.mssql.repository.EmployeeRepository;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@GetMapping("/employees")
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees() {
return employeeRepository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/employees/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Employee> getEmployeeById(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId)
throws ResourceNotFoundException {
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(employee);
}
@PostMapping("/employees")
public Employee createEmployee(@Valid @RequestBody Employee employee) {
return employeeRepository.save(employee);
}
@PutMapping("/employees/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Employee> updateEmployee(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId,
@Valid @RequestBody Employee employeeDetails) throws ResourceNotFoundException {
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));
employee.setEmailId(employeeDetails.getEmailId());
employee.setLastName(employeeDetails.getLastName());
employee.setFirstName(employeeDetails.getFirstName());
final Employee updatedEmployee = employeeRepository.save(employee);
return ResponseEntity.ok(updatedEmployee);
}
@DeleteMapping("/employees/{id}")
public Map<String, Boolean> deleteEmployee(@PathVariable(value = "id") Long employeeId)
throws ResourceNotFoundException {
Employee employee = employeeRepository.findById(employeeId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee not found for this id :: " + employeeId));
employeeRepository.delete(employee);
Map<String, Boolean> response = new HashMap<>();
response.put("deleted", Boolean.TRUE);
return response;
}
}11. Running Application
This spring boot application has an entry point Java class called SpringBootCrudRestApplication.java with the public static void main(String[] args) method, which you can run to start the application.
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication is a convenience annotation that adds all of the following:
- @Configuration tags the class as a source of bean definitions for the application context.
- @EnableAutoConfiguration tells Spring Boot to start adding beans based on classpath settings, other beans, and various property settings.
- Normally you would add @EnableWebMvc for a Spring MVC app, but Spring Boot adds it automatically when it sees spring-webmvc on the classpath. This flags the application as a web application and activates key behaviors such as setting up a DispatcherServlet.
- @ComponentScan tells Spring to look for other components, configurations, and services in the hello package, allowing it to find the controllers.
The main() method uses Spring Boot’s SpringApplication.run() method to launch an application.
>> Spring Boot 2 REST APIs Integration Testing
12. Integration Testing for REST APIs
There is a separate beautiful article for integration testing for REST APIs on:>> Spring Boot 2 REST APIs Integration Testing
13. Testing REST APIs via Postman Client
1. Create Employee REST API
HTTP Method: POST
Request URL: http://localhost:8080/api/v1/employees
Note that request and response JSON in the above diagram, the response contains database auto generated id.
2. Get Employee by ID REST API
HTTP Method: GET
Request URL: http://localhost:8080/api/v1/employees/11
5. Delete Employee REST API
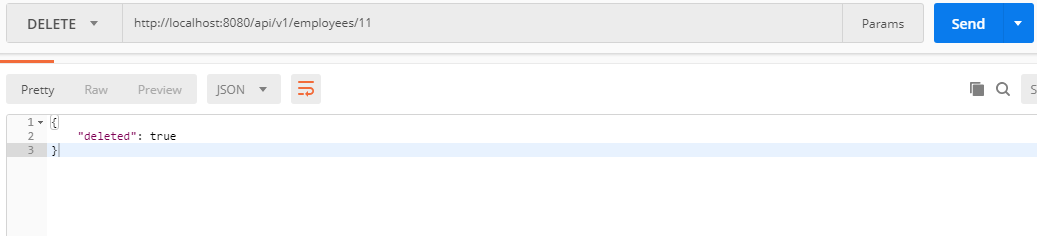
HTTP Method: DELETE
Request URL: http://localhost:8080/api/v1/employees/11
14. Source code on GitHub
The source code of this tutorial is available on my GitHub repository.







Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment