📘 Premium Read: Access my best content on Medium member-only articles — deep dives into Java, Spring Boot, Microservices, backend architecture, interview preparation, career advice, and industry-standard best practices.
🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (176K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
Creating Named Queries
Create Spring Boot Project
The pom.xml File
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>net.guides.springboot2</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-testing-examples</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>springboot-testing-examples</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4</version>
<relativePath/>
<!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
- It collects all the jars on the classpath and builds a single, runnable "über-jar", which makes it more convenient to execute and transport your service.
- It searches for the public static void main() method to flag as a runnable class.
- It provides a built-in dependency resolver that sets the version number to match Spring Boot dependencies. You can override any version you wish, but it will default to Boot’s chosen set of versions.
JPA Entity - User.java
import java.util.Date;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "users")
@NamedQuery(name = "User.findByEmailAddress", query = "select u from User u where u.emailAddress = ?1")
@NamedQueries(value = {
@NamedQuery(name = "User.findByLastname", query = "select u from User u where u.lastname = ?1")
})
public class User {
private long id;
private String firstname;
private String lastname;
private Date startDate;
private String emailAddress;
private int age;
private int active;
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstname() {
return firstname;
}
public void setFirstname(String firstname) {
this.firstname = firstname;
}
public String getLastname() {
return lastname;
}
public void setLastname(String lastname) {
this.lastname = lastname;
}
public Date getStartDate() {
return startDate;
}
public void setStartDate(Date startDate) {
this.startDate = startDate;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getActive() {
return active;
}
public void setActive(int active) {
this.active = active;
}
public String getEmailAddress() {
return emailAddress;
}
public void setEmailAddress(String emailAddress) {
this.emailAddress = emailAddress;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", firstname=" + firstname + ", lastname=" + lastname + ", startDate=" + startDate +
", emailAddress=" + emailAddress + ", age=" + age + ", active=" + active + "]";
}
}
- The User class is annotated with @Entity, indicating that it is a JPA entity.
- The User’s id property is annotated with @Id so that JPA will recognize it as the object’s ID. The id property is also annotated with @GeneratedValue to indicate that the ID should be generated automatically.
@NamedQuery
@Entity
@Table(name = "users")
@NamedQuery(name = "User.findByEmailAddress", query = "select u from User u where u.emailAddress = ?1")
public class User {
}
@NamedQueries
@Entity
@Table(name = "users")
@NamedQueries(value = {
@NamedQuery(name = "User.findByLastname", query = "select u from User u where u.lastname = ?1") })
public class User {
}
Spring Data JPA Repository - UserRepository.java
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import net.guides.springboot2.springboottestingexamples.model.User;
/**
* UserRepository demonstrates the method name query generation.
*
* @author Ramesh Fadatare
*
*/
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository < User, Long > {
User findByEmailAddress(String emailAddress);
List < User > findByLastname(String lastname);
}
Create an Application class
package net.guides.springboot2.springboottestingexamples;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import net.guides.springboot2.springboottestingexamples.model.User;
import net.guides.springboot2.springboottestingexamples.repository.UserRepository;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String...args) throws Exception {
User user = new User();
user.setActive(1);
user.setAge(28);
user.setEmailAddress("ramesh24@gmail.com");
user.setFirstname("Ramesh");
user.setLastname("Fadatare");
user.setStartDate(new Date());
user = userRepository.save(user);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------:: " + user.getId());
System.out.println(" ---------------@NamedQuery ---------------------");
System.out.println("--------------findByEmailAddress -----------------");
User user2 = userRepository.findByEmailAddress("ramesh24@gmail.com");
System.out.println(user2.toString());
System.out.println(" ---------------@NamedQuery ---------------------");
System.out.println("--------------findByLastname -----------------");
List < User > user3 = userRepository.findByLastname("Fadatare");
System.out.println(user3.get(0).toString());
}
}
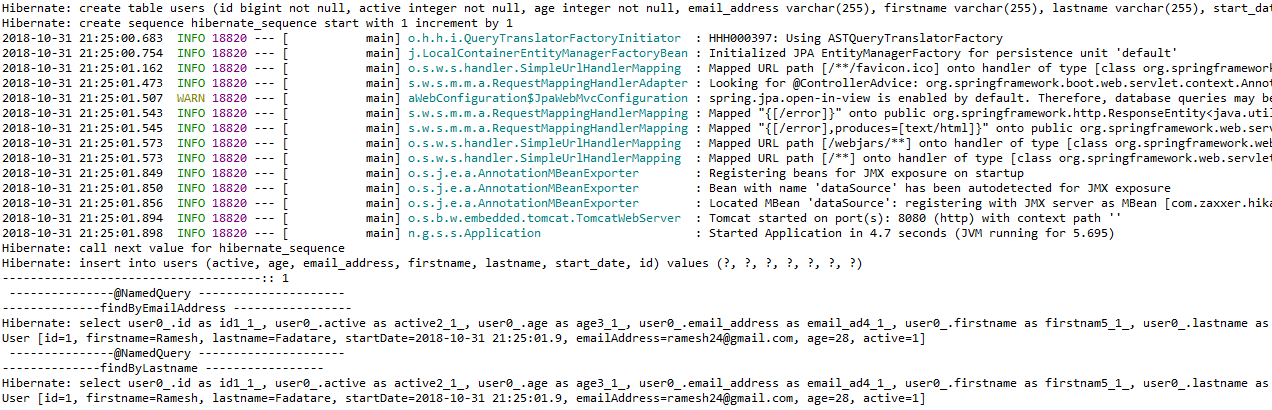
Running Application
java -jar target/spring-data-jpa-example-0.1.0.jar
Output
Source code of this article available on my GitHub repository - https://github.com/RameshMF/spring-data-jpa-tutorial




![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)










Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment