In this tutorial, we will learn how to build CRUD RESTful API using Spring Boot 3, Spring Data JPA (Hibernate), and MySQL database.
CRUD stands for "create, read, update, and delete," which are the four basic functions of persistent storage. Spring Boot is a Java-based framework used to build web applications and RESTful APIs. Together, Spring Boot and CRUD can be used to quickly develop a RESTful API that can create, read, update, and delete data in a database.
Learn complete Spring boot at Learn and Master Spring Boot
Spring Boot Project Architecture
We are going to use three-layer architecture in our Spring boot project:
Tools and Technologies Used:
- Spring Boot 3.0
- Java 17
- Spring Data JPA
- Hibernate
- MySQL Database
- Maven
- Postman
1. Create and Setup Spring Boot Project in IntelliJ
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-restful-webservices</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-restful-webservices</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot Restful Webservices</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
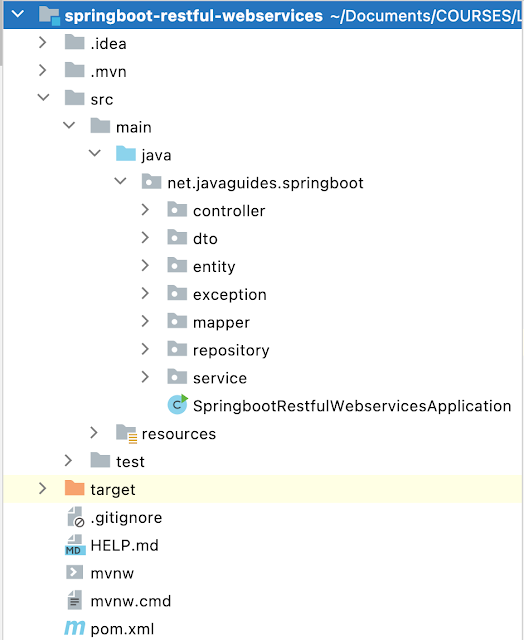
</project>Project Structure
create database user_managementspring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user_management
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=Mysql@123
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=updateMake sure that you change the spring.datasource.username & spring.datasource.password properties as per your MySQL installation.
In the above properties file, the last two properties are for Hibernate. Spring Boot uses Hibernate as the default JPA implementation.
The property spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto is used for database initialization. I’ve used the value “update” for this property to create the database tables automatically.
Create User JPA Entity
package net.javaguides.springboot.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Entity
@Table(name = "users")
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String firstName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String lastName;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String email;
}Create Spring Data JPA Repository - UserRepository
package net.javaguides.springboot.repository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
}Create Service Layer
Service Interface
Let's create an UserService interface and declare the following CRUD methods:
package net.javaguides.springboot.service;
import net.javaguides.springboot.entity.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserService {
User createUser(User user);
User getUserById(Long userId);
List<User> getAllUsers();
User updateUser(User user);
void deleteUser(Long userId);
}UserServiceImpl
package net.javaguides.springboot.service.impl;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import net.javaguides.springboot.entity.User;
import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.UserRepository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.service.UserService;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.util.Strings;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Optional;
@Service
@AllArgsConstructor
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public User createUser(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
@Override
public User getUserById(Long userId) {
Optional<User> optionalUser = userRepository.findById(userId);
return optionalUser.get();
}
@Override
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public User updateUser(User user) {
User existingUser = userRepository.findById(user.getId()).get();
existingUser.setFirstName(user.getFirstName());
existingUser.setLastName(user.getLastName());
existingUser.setEmail(user.getEmail());
User updatedUser = userRepository.save(existingUser);
return updatedUser;
}
@Override
public void deleteUser(Long userId) {
userRepository.deleteById(userId);
}
}Create Controller Layer - UserController
We’ll now create the REST APIs for creating, retrieving, updating, and deleting a User resource.Let's create UserController class and let's build CRUD REST APIs for the User resource:
package net.javaguides.springboot.controller;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import net.javaguides.springboot.entity.User;
import net.javaguides.springboot.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@AllArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("api/users")
public class UserController {
private UserService userService;
// build create User REST API
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<User> createUser(@RequestBody User user){
User savedUser = userService.createUser(user);
return new ResponseEntity<>(savedUser, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
// build get user by id REST API
// http://localhost:8080/api/users/1
@GetMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity<User> getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long userId){
User user = userService.getUserById(userId);
return new ResponseEntity<>(user, HttpStatus.OK);
}
// Build Get All Users REST API
// http://localhost:8080/api/users
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<List<User>> getAllUsers(){
List<User> users = userService.getAllUsers();
return new ResponseEntity<>(users, HttpStatus.OK);
}
// Build Update User REST API
@PutMapping("{id}")
// http://localhost:8080/api/users/1
public ResponseEntity<User> updateUser(@PathVariable("id") Long userId,
@RequestBody User user){
user.setId(userId);
User updatedUser = userService.updateUser(user);
return new ResponseEntity<>(updatedUser, HttpStatus.OK);
}
// Build Delete User REST API
@DeleteMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity<String> deleteUser(@PathVariable("id") Long userId){
userService.deleteUser(userId);
return new ResponseEntity<>("User successfully deleted!", HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
Running Spring Boot Application
Run the spring boot application from IDE:From your IDE, run the SpringbootRestfulWebservicesApplication.main() method as a standalone Java class that will start the embedded Tomcat server on port 8080 and point the browser to http://localhost:8080/.
Run the spring boot application using the command line:
Just go to the root directory of the application and type the following command to run it -
$ mvn spring-boot:run
The application will start at Spring Boot’s default tomcat port 8080.
Test CRUD RESTful WebServices using Postman Client
Create User REST API:
Request Body:
{
"firstName": "ramesh",
"lastName":"fadatare",
"email": "ramesh@gmail.com"
}Get User REST API:
Update User REST API:
Request Body:
{
"firstName": "ram",
"lastName":"fadatare",
"email": "ram@gmail.com"
}Get All Users REST API:
DELETE User REST API:
Source Code on GitHub
Conclusion
Further Reading
- Spring Boot DTO Example Tutorial
- Spring Boot ModelMapper Example
- Spring Boot MapStruct Example Tutorial
- Deploy Spring Boot Application on Docker
- Spring Boot 3 Tutorial
- Spring Boot CRUD RESTful WebServices with MySQL Database
- Spring Boot DTO Example Tutorial
- Spring Boot ModelMapper Example - Map Entity to DTO
- Spring Boot MapStruct Example Tutorial
- Spring Boot MySQL Docker Compose Example
- Deploy Spring Boot MySQL Application to Docker








Very nice step by step instructions. Loved your articles.
ReplyDeleteEnjoyed learning. Thanks for the great tutorial.
ReplyDeleteExcellent tutorial for beginners to quickly start spring boot application development.
ReplyDeleteThank you so much.. can you share your database file with me
ReplyDeleteYou can get it from my Github repository, the link given at end of this tutorial. Cheers.
Deletecan you share your database file with me? there isnt in the github repo
ReplyDeleteHi sir, Please give the solution for below issue while implementing your application.
ReplyDeleteField employeeRepository in com.example.demofirst.controller.EmployeeController required a bean of type 'com.example.repository.EmployeeRepository' that could not be found.
The injection point has the following annotations:
- @org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)
Action:
Consider defining a bean of type 'com.example.repository.EmployeeRepository' in your configuration.
Hi sir, Please give the solution for below issue while implementing your application.
ReplyDeleteField employeeRepository in com.example.demofirst.controller.EmployeeController required a bean of type 'com.example.repository.EmployeeRepository' that could not be found.
The injection point has the following annotations:
- @org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)
Action:
Consider defining a bean of type 'com.example.repository.EmployeeRepository' in your configuration.